LiDAR Sensor Models
This page provides an overview of LiDAR sensor principles and presents the models that are available in Speos.
A LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a system composed of a light source (an emitter channel - Tx) and a sensor (a receiver channel - Rx) meant to measure the distance to a target by sending pulsed laser light. The emitter illuminates a target by sending laser pulses and evaluates the distance to that target based on the time the reflected pulse took to hit the receiver. LiDAR technology is widely used in the automotive industry as it holds a key role in the development of autonomous vehicles by being able to detect and render a model of a vehicle's surroundings.
Three different types of LiDAR sensors are available to cover different needs and configurations.
Types of LiDAR Sensors
Static
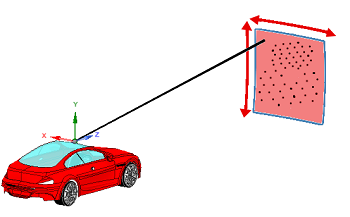
Solid-State or flashing LiDARs are static systems with no moving parts. With a camera-like behavior, the flashing LiDAR sends one large laser pulse in one direction to detect and model its environment.
This type of LiDAR, however, rarely exceeds a 120° field of view.
Scanning
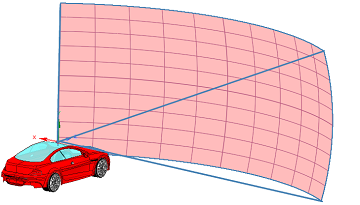
Scanning LiDAR systems use dual-axis mirrors to deflect laser beams into specific scanning angles. With this type of LiDAR, you can define a custom beam detection pattern by describing the azimuth and elevation shooting angles of the LiDAR. These systems have a detection range that strongly depends on the optical components and the field of view of the imager. They can cover, at most,180 degrees.
Rotating
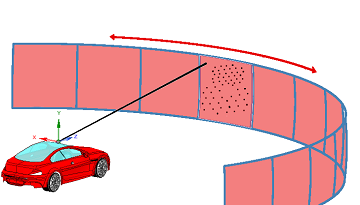
Rotating LiDARs are systems with a mechanical rotation offering controlled aiming directions over a 360 field of view. This type of LiDAR enables a multi-direction detection and a high speed scanning.
With this configuration, the scanning pattern is repeated sequentially for each rotation step of the LiDAR.
In Speos
- From solid-state to rotating LiDARs, define LiDAR systems based on currently commercialized LiDAR models.
- Manage all the characteristics of your LiDAR system: its energy, range, emission pattern etc.


