Creating an Optical Lens
This page shows how to create optical lenses.
To create an Optical Lens:
- From the Design tab, click Optical Lens
_Optical_Lens.png) and select a lens type/shape (Rectangular, Circular,
Honeycomb, Stripes, Freestyle).
and select a lens type/shape (Rectangular, Circular,
Honeycomb, Stripes, Freestyle). -
In General, from the Source Type drop-down list, select:
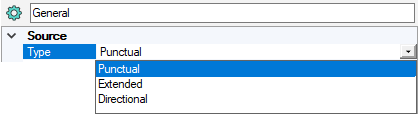
- Punctual to position the source by selecting a point in the 3D view.
- Extended to select an emitting surface like a filament, cylinder, LED, chip etc.
-
Directional to define the direction of the rays by clicking a line in the 3D view.
In case of Directional source, the rays are collimated. A yellow arrow indicates the light direction. If needed, use Reverse direction to adjust the direction of the rays.
If you select Extended, you can define the Flux of the source.
The Flux will be used to run the Photometry tool simulation that generates a photometric preview displayed in the feature viewer, a HTML report and a XMP file of the selected element(s) of the feature.
For more information on the Photometry tool, refer to Understanding Display Properties.
- Define the Refractive index of the medium from which the light comes.
-
To define the support:
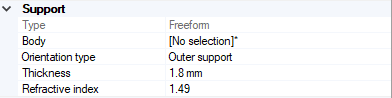
Important: When computing the Optical Lens, the support is meshed. The bigger the support, the longer the computation of the feature. We recommend you to define a support size as close as possible to the feature size.-
Click
_OPD_Support_Surface.png) to select a surface
in the 3D view.Note: A face or a multifaces body can be selected as surface.
to select a surface
in the 3D view.Note: A face or a multifaces body can be selected as surface. -
Define the Orientation type of the support, that is on which side of the surface the elements will be created:
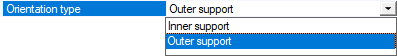
- Select Outer support to consider the outer surface as the support and create the elements on the inside.
-
Select Inner support to consider the inner face as the support and create the elements on the outside.
Note: The principle of inner and outer surface is determined by the source position. The source is always facing the inner surface of the support.
- If needed, adjust the Thickness of the support. This value is used to define an intermediary surface carrying the elements.
- Define the Refractive index of the lenses.
-
-
In Target, if you want to verify that your current design passes regulation standards, select a XML Template corresponding to the regulation standard.
The XML template will be used by the Photometry tool simulation to generates the photometric preview displayed in the feature viewer, the HTML report and the XMP file of the selected element(s) of the feature.
Note: You can find existing XML templates of regulation standards in the Ansys Optical Library.For more information on the Photometry tool, refer to Understanding Display Properties.
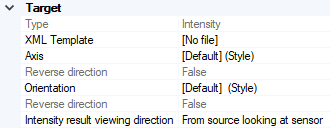
From the Type drop-down list, select the type of metrics used for reviewing the beam pattern:
If the area to light is in a plane placed at a known distance from the source, select Illuminance.
Light is focalized in one point/plane. The viewer displays illuminance values.
If the area to light is defined angularly, select Intensity.
Light is directed in a given direction. The viewer displays intensity values.
- If you want to define specific axes for the sensor, in the 3D view click
_Projection_Axis.png) to select a projection axis and
to select a projection axis and _OPD_Optical_Axis.png) to select an orientation axis or click
to select an orientation axis or click _Axis_System_Autofill.png) and select a coordinate
system to autofill the Axis System.
and select a coordinate
system to autofill the Axis System. - In case of an Illuminance target, define the integration direction of the sensor with Reverse integration direction if necessary. The Integration direction (non visible in 3D view) should be in the opposite direction of the target axis (red arrow). The target axis should face the Optical Lens.
In Intensity result viewing direction:
- Select From source looking at sensor to position the observer point from where light is emitted.
- Select From sensor looking at source to position the observer in the opposite of light direction.
In the Style tab, set the axis system of the grid define the distribution, pattern and size of the elements to be created on the support.
Note: If you define manually one axis only, the other axis is automatically (and randomly) calculated by Speos in the 3D view. However, the other axis in the Definition panel may not correspond to the axis in the 3D view. Please refer to the axis in the 3D view.-
In Manufacturing, activate the drafting of the elements if you want mechanical constraints coming from unmolding to be taken into account.
If activated, define a Draft length in mm. The draft length defines the sewing surface created between two adjacent faces.
- From the Design tab, click Compute
_Compute.png) to generate the lenses.
to generate the lenses.
Optical Lenses are created are built in the 3D view. You can edit the lens at any time. The generation time of the Optical Lens depends on the complexity of the settings.


