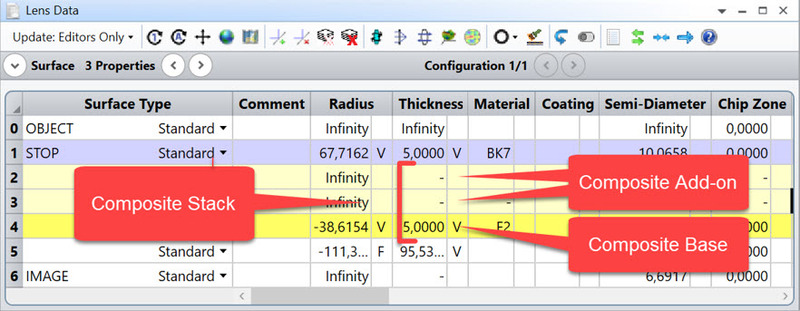
Composite Surface
The Composite property allows the sag of most sequential surface types to be added together to create a summed, or "Composite", surface.

Any number of surfaces can be added together (these are referred to as "Composite Add-on", or simply "Add-on"). The sag profile of the Add-on surfaces will be added to the following Add-on surface, and the total sag will finally be added to the first non-composite surface (referred to as "Composite Base", or simply "Base") that follows the Add-ons. The Base surface profile will then be the summation of all the Add-on profiles, plus its own profile. The overall surface resulting from the sum of Add-On and Base is referred to as "Composite Stack", or simply "Composite".
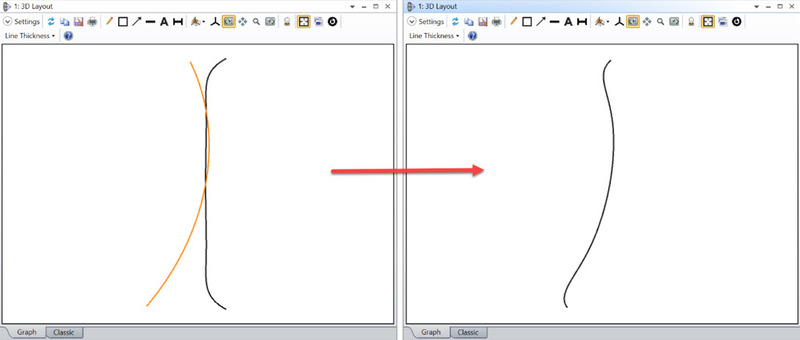
For example, adding the two surfaces below on the left hand side, the complex shape in the right hand side can be created:
A surface can be made into a Composite Add-on by checking the box next to "Composite Surface: Add sag to next surface". When on, the sag of the surface is added to the surface that follows in the LDE. The Add-on row color is changed to light yellow and the Base row is shown in dark yellow. The total sag resides in the Base surface, which is the only surface that participates in the raytrace; rays do not interact with the Composite Add-on surfaces used to create the final shape. Similarly to normal, non-composite surfaces, the default semi-diameter of the Composite Add-ons is based on ray incident position calculations, but can be overwritten by the user. If an Aperture is set on the Base, this will be the Aperture for the whole Composite surface.
Composite Surface: Add sag to next surface: Makes the surface a Composite Add-on
Set Tilt/Decenter to follow Base surface aperture: Automatically populate tilt and decenter values to ensure surface is positioned at the center of the off-axis aperture of the Base surface (see details below)
Update Tilt: Automatically updates tilt values to reflect the surface orientation at the specified decenters (see details below)
Decenter X: The X-decenter of the surface with respect to the Composite Base
Decenter Y: The Y-decenter of the surface with respect to the Composite Base
Decenter Z: The Z-decenter of the surface with respect to the Composite Base
Tilt X: The X-tilt of the surface with respect to the Composite Base
Tilt Y: The Y-tilt of the surface with respect to the Composite Base
Tilt Z: The Z-tilt of the surface with respect to the Composite Base
Note: To make the sum possible, the Add-on and Base sags being added must be in the same coordinate system. In this respect, tilt values, when present, are always defined with respect to the coordinate system of the Base surface, or to center of the off-axis aperture when decenter values are specified.
The Add-on composite surface can't be set as stop to aperature. The add-ons are not participating in the ray trace. The sag profile of the add-on composite surfaces will beadded to the following auxillary add-on or base composite surface.
Add-on surfaces won't be visible in Layout and Shaded Model, only the Composite stack resulting from the sum of Add-ons and Base surfaces will be. In future releases a visualization tool for Add-on surfaces will be implemented. Decenter Z will define the visual separation between each Add-ons. Until implementation of the visualization tool, this property will be greyed out and unavailable to users. Note that Decenter Z does not contribute to overall system length.
Surface types that can be used as Composite Add-On surfaces can also be used as Composite Base. Supported surfaces are listed in the table below, the composite checkbox is unavailable for all other surface types.
Supported Surfaces
-
Biconic
-
Biconic Zernike
-
Chebyshev Polynomial
-
Cubic Spline
-
Even Asphere
-
Extended Asphere
-
Extended Cubic Spline
-
Extended Odd Asphere
-
Extended Polynomial
-
Grid Sag
-
Irregular
-
Odd Asphere
-
Odd Cosine
-
Off-Axis Conic Freeform
-
Periodic
-
Polynomial
-
Q-Type Asphere
-
Q-Type Freeform
-
Radial NURBS
-
Standard
-
Superconic
-
Tilted
-
Torodial
-
Toroidal NURBS
-
TrueFreeForm
-
Zernike Fringe Sag
-
Zernike Standard Sag
-
Zernike Annular Standard Sag
Adding Add-on surfaces off-axis
When an off-axis Aperture is defined on the Base, users can use the "Set Tilt/Decenter to follow Base surface aperture" button to positions the Composite Add-on surfaces at the center of the off-axis aperture of the Base. OpticStudio will populate automatically tilt and decenter values under Composite to ensure alignment. Decenters match the vertex location of the Base surface, as specified in its Aperture property. Tilts match the orientation of the Base surface at the center of the off-axis aperture. If present, any existing tilt/decenter values will be overwritten.
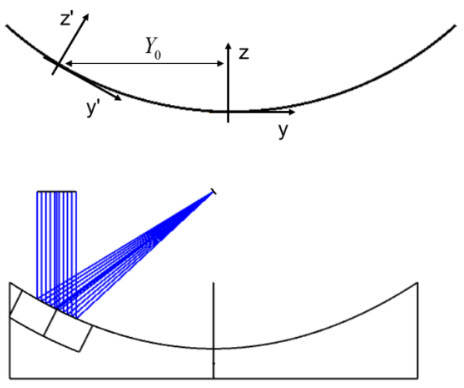
In case decenters are manually specified, the "Update Tilt" button can be used to automatically populate tilt values so that the Add-on orientation matches the one of the Base surface at the specified decenter.
If more than one Add-on is present in the Composite Stack, all Add-on surfaces will be stacked according to the Tilts and Decenters specified in the Composite properties of the lowest Add-on in the LDE. All other Add-on surfaces will have all Tilts and Decenters under Composite greyed out, as Add-on surfaces cannot be moved with respect to one another. This limitation might be removed in future releases.
Decenter Z is greyed out for present release, but will be available in future ones to allow visualization of the Add-on surfaces
General comments on using Composite Surfaces:
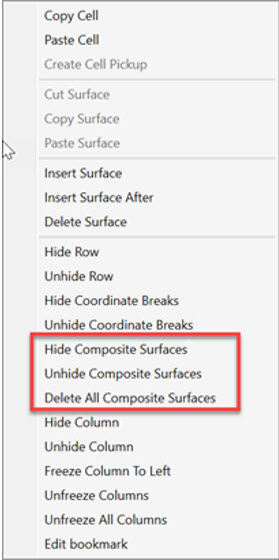
To avoid cluttering the Lens Data Editor, the option to delete, hide or unhide Composite Add-on surfaces is available in the right-click menu of the Lens Data Editor.
While the Composite surface per se, represented for raytracing purposes by the Composite Base, is treated by OpticStudio like any other surface, Composite Add-on surfaces are not directly considered for raytracing. Therefore, data for these surfaces won't appear in the Single Raytrace analysis. Similarly, any Merit Function operand based on Raytracing data is not relevant and will return zero if applied to Add-on surfaces.
Global coordinates for the Base surface will be calculated and displayed in the Prescription Data, but not for the Composite Add-on surfaces, which are in the coordinate system relative to the Base specified by the Decenters and Tilts above.
Because the Add-on surfaces are physically one with the Base, tolerancing operands such as TSDX or TIRY that imply a misalignment in tilt, decenter or roll between the Add-ons and the Base are disabled for Add-ons.
Composite surfaces are currently not supported by the "Convert to NSC Group" button in the File tab and cannot be converted into nonsequential systems.
Next:


