High Performance Computing (HPC) Integration
Ansys Electromagnetics products offer direct integration with a number of High Performance Computing (HPC) software programs (job schedulers). This direct integration does not require the RSM service. The list of currently-supported HPC software includes:
You can also do custom integration.
For additional information about high performance computing not in this guide, see the Ansys Electromagnetics HPC Administrator's Guide (HPC_Admin.pdf) in "<install_dir>\ANSYS Inc\v251\AnsysEM\Help".
A job scheduler may also be described as a batch system, a Distributed Resource Management System (DRMS) or Distributed Resource Manager (DRM). The features supported on each scheduler are included in the documentation for each. For each job scheduler, the versions or revisions that have been tested are included.
You can submit jobs using the command line tools or other tools provided by the scheduler. Ansys Electromagnetics products include a Submit Job To dialog box such as the example shown below to help you submit jobs to a job scheduler.
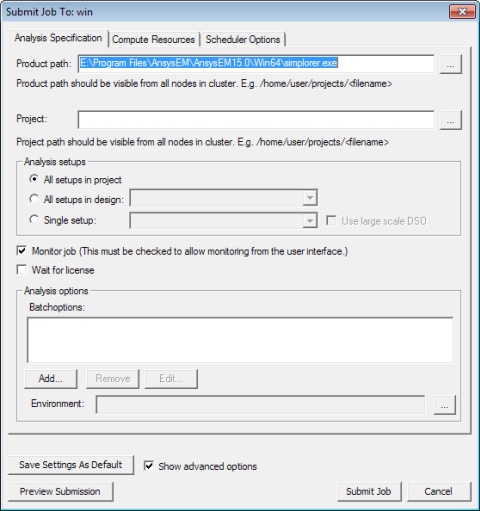
The general procedure is to specify the scheduler and head node, describe and submit the job, and monitor the results.
The Submit Job To dialog box contains three tabs:
- Analysis Specification – Specify the project name, the setups, and analysis options such as batchoptions. If Show advanced options is selected, environment variables can also be added. The project file path name must be a UNC path that is accessible from each compute host used for Ansys Electromagnetics jobs.
- Compute Resources – Specify either a predefined analysis configuration (see Configuring Distributed Analysis) or specify parameters in the Resource selection fields. Job parallelization settings are enabled if supported by the chosen scheduler.
- Scheduler Options (not present for RSM jobs) – Specify the job name and priority. If Show advanced options is selected, additional job submission options can be set.
When you use the GUI to submit jobs, the Desktop (UI) process must run on a host which is also a submission host for the job scheduler. This mode is called local mode or working mode.
Import and Export Configurations
The bottom of the job submission interface has buttons for Import, Export, and Import Configuration let you save a configuration for each solver type.
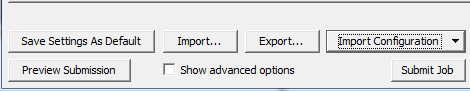
- Click Export to export most of the settings of this dialog box (all tabs) to a file.
- Click Import to update most of the settings in this dialog box (all tabs) from a file.
- Click Import Configuration to update
the DSO settings in this dialog box from any DSO configuration as shown
in the Configurations tab of the HPC and Analysis Options
dialog box. The Design Type of the DSO configuration must match the design
type of one of the designs in the project, so the project must be specified
before using the Import Configuration button. The batchoptions
are also set from the specified DSO configuration or from the Design
Type options settings, which are shown in the Options tab of the
HPC and Analysis Options dialog box.
Click Export and Import to save and restore a frequently used collection of job submission settings. You can also click Save Settings as Default to save the current settings, but it always overwrites any previously saved settings. When you click Export, you can save multiple sets of settings, or may transfer the settings to another machine.
The Select Scheduler dialog box also has Export and Import buttons. Use these buttons to save the settings in this dialog box to a file or restore them from a file.
An exported configuration is named Submit_Job_Settings by default and has an .areg extension. A file browser window opens in the project folder and lets you name an exported file and location, and select .areg files to import. The SubmitJob scripting command uses job submission settings that have been exported from the Submit Job dialog box to an .areg file. The path to this .areg file is thus the first argument to the SubmitJob scripting command. For further information, see Job Submission Scripting.
Related Topics