Computing Frequency Sweep
Frequency sweep analysis allows you to evaluate the effects on the voltage and current distribution of applied AC voltage and current sources on your design across a specified frequency range. In a sweep operation, the frequency of the sources is swept from a minimum value to a maximum value. You can set the start frequency, stop frequency, and number of frequency points used. The analysis can use voltage/current sources defined in SIwave, or sources accessed via push excitations from Ansys Electronics Desktop.
Results are expressed graphically with the use of frequency response plots. Frequency responses show how the amplitude and phase of user-defined voltage probes change with different frequencies. The software also displays a 3D plot of the magnitude of the voltage difference between a specified pair of planes.
During a frequency sweep, voltage and current sources remain active, and all ports are ignored.
To generate a frequency sweep:
- Click Simulation.
- From the SIwave area, click Compute Frequency Sweeps.
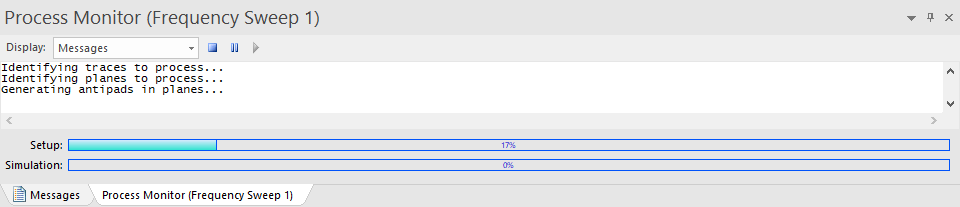
- Specify the source of the excitations. You can select one of the following options:
- Use sources defined in the project
- Use sources defined in an external file. Click Browseand locate the external source file. This file specifies the ports at which the frequency dependent sources will be attached. If an external file is used, any sources you placed in the layout are ignored.
- Enter values for Start Frequency, Stop Frequency, and Number of Solution Points.
- From the Distribution field, select one of:
- Linearly – the difference between the start frequency and the stop frequency is calculated and is divided by the number of solution points.
- By Decade – distributes the number of points specified logarithmically, over each decade.
- To add or delete frequency points, use the Add Above, Add Below, and Delete Selection buttons.
- To preview all frequency points, click Preview.
- Clock Close to exit the Frequency List Preview.
- To save grid values to a file, click Save. Choose a file name and location for your SIwave Frequency Sweep Distribution File (*.sfsdf).
- To load grid values from an SIwave Frequency Sweep Distribution File (*.sfsdf), click Load and select your file.
- To make the current settings the default, click Set Default. When a default value has been set, the window for that simulation type will always be populated with those settings when the window is opened.
- To remove the default settings, click Clear Default.
- From the Voltage Surface Plot Options area, use the drop-down menus to select the layers between which voltage difference is to be plotted.
- If you want to save these settings for subsequent simulations, click Save Settings.
- To see additional solver options, click Other Solver Options.
- Click Launch to run the simulation.
The Compute Frequency Sweep window appears.
Additionally, you can also specify the termination resistors for other ports, voltage source resistance values, or current source resistance values in this file.
If you select an external file, the Interpolate spectrum at missing frequency points check box is enabled. If SIwave cannot find a value at a certain frequency f in the external excitation file during simulation, it generates a value by interpolating the data specified at the two closest frequency points straddling f. If this option is unchecked, no simulation data is computed at the frequency point f for which excitation data is absent.
The Frequency List Preview window appears, showing all the points.
The Messages window updates with a Process Monitor tab that displays the progress.