Enabling GPU (Beta)
Ansys Electronics Desktop supports GPU acceleration for
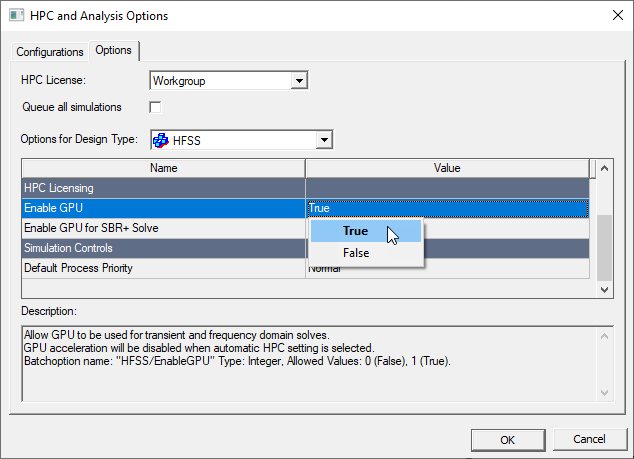
To enable use of GPU or MIC acceleration, you can set Enable GPU to True and set Use Automatic Settings to off in the Analysis Configuration window. The matrix solver automatically determines if all cores should be used, or if one GPU should be used to give the best performance. For example, for a Maxwell Eddy Current Solution Matrix, if you specify 4 cores for the simulation, the 3D Eddy current solver will use 4 cores in parallel during matrix assembly while the matrix solver will use either 4 cores or 1 GPU.
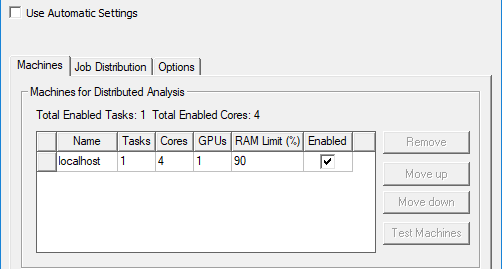
To enable use of GPU, you can set Enable GPU to True and specify the number of GPUs in the Analysis Configuration window.

nvidia-smi.exe -q
.To change compute mode, run the following command:
nvidia-smi -i 0 -c 0
-i= device id. Device id is an integer value. It correlates with number of GPUs present in the machine.-c= compute mode. Compute mode can be 0 or 1. 0 = default or 1 = exclusive mode.
For solvers that can use GPUs, when you uncheck Use Automatic Settings, the analysis configuration lets you specify the number of GPUs to be used by each machine, along with the existing settings for cores and RAM Limit. This makes sense, because GPUs, cores, and RAM are all resources that the user is managing, and GPUs and cores both contribute to HPC count. Each machinehas tasks and GPUs. The GPUs are distributed among the tasks, similarly to how cores are distributed. For example, if a machine has 3 tasks and 2 GPUs, then the first two tasks will get one GPU each, and the third task will get no GPU.
For design types like HFSS that support GPU for different types of solve (frequency, transient, SBR+), the GPU setting when Use Automatic settings is unchecked applies to all types. To use GPU for some solves and not for others, you can create multiple configurations.
Determining When a GPU or MIC is Being Used
You can determine if a GPU or MIC is being used for acceleration by viewing the Solutions dialog box, Profile tab. If a GPU is successfully locked for use by the solver process, the profile shows the GPU's CUDA device ID and its name.

If the GPU is not used, the Solution Profile indicates that, and the CPU cores are used.
When GPU is used:
- GPU must be enabled for HFSS/Maxwell.
- Both Windows and Linux are supported.
- Only complex symmetric matrices can be solved by CUDA.
- Matrix must be large enough. By default, its dimension should be larger than 2,000,000.
- The times using CUDA and CPU only are estimated. If GPU is faster, it will be used. If not, the solver falls back to multi-core CPU.
PU and CPU:
- The estimation is based on the structure of the matrix, not just the dimension.
- The generation and model of GPU are considered. The newer the model is, the faster the GPU estimation is.
- The clock rate and number of cores of CPU are considered. The higher the rate is, the more the cores are, the faster the CPU estimation is.
- Finally, the faster device (GPU or CPU) is selected based on the estimation.
Why GPU is Not Used
- The estimation is based on the whole matrix, not just the size. Having larger matrices doesn’t mean GPU will be used.
- The bandwidth is not useful either. It is possible to have two matrices with exactly the same size and bandwidth, one favoring GPU and the other CPU.
- If GPU is of older models while CPU is not, GPU may not be used.
- If CPU has high clock rate, GPU may not be used.
- If CPU has many cores, GPU may not be used.
- If Use Automatic settings in Analysis Configuration is checked.
- Nvidia GPU drivers are downloaded from certain repository (e.g. RedHat) instead of directly from Nvidia website
Multiple GPUs
When there are multiple GPU cards in the same machine, the first solver process (hf3d, 3dedy) locks the first GPU card available (not locked or used by other processes, not used for display, etc.), the second process locks the second card available, and so on. After all cards are locked, solver uses CPU only.
