Core Loss Coefficient Extraction from Single-Frequency Loss Curve
The principles of the computation algorithm for Kh, Kc, Ke, and Y are summarized as below.
The iron-core loss without DC flux bias is expressed as the following:
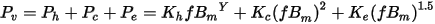
where f is the frequency, and Bm is the amplitude of the applied sinusoidal flux density waveform. The classical eddy-current loss coefficient Kc can be calculated analytically from
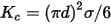
where s is the conductivity, and d is the thickness of one lamination sheet.
The remaining coefficients Kh and Ke, as well as Y, can be derived by minimizing the error between the measured and modeled core loss curves at different Bm expressed as
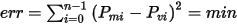
where Pmi and Pni are the measured and modeled core losses at a fixed frequency f and varied flux density amplitudes Bmi, and n is the number of points of the measured core loss curve. Kc is known, so the modeled core loss Pni depends on unknown parameters Kh, Ke, and Y. Kh and Ke can be identified by linear regression, and Y by a numerical optimization algorithm. Assuming an initial value of Y, the error can be derived from
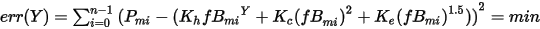
After Kh and Ke have been determined by linear regression, the error is a function of Y. The optimal Y can be finally derived by applying a numerical optimization algorithm to minimize the error.
Related Topics
Core Loss Model for a Maxwell Material
Calculating Properties for Core Loss BP Curve
Core Loss Coefficient Extraction from Single-Frequency Loss Curve
Core Loss Coefficient Extraction from Multi-Frequency Loss Curves
Core Loss Coefficients for Electrical Steel
