The Mesh Generation Process
Following is the general mesh generation process:
- An initial mesh is generated and includes surface approximation settings. If necessary, the mesher will automatically perform any repairs needed to recover an accurate mesh representation of a model. The solution profile will indicate when mesh repairs have been made, and the results of these repairs will be displayed per object in the mesh statistics panel.
- If lambda refinement was requested, the initial mesh is refined based on the material-dependent wavelength.
- Any mesh operations that were defined are used to refine the mesh.
- If ports were defined, the 2D mesh is refined iteratively.
- Using the resulting mesh, the electromagnetic fields are computed that exist inside the structure when it is excited at the solution frequency.
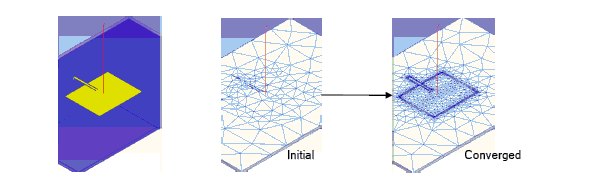
- If you are performing an adaptive analysis, the current finite element solution is used to estimate the regions of the problem domain where the exact solution has strong error. Tetrahedra in these regions are refined.
- Another solution is generated using the refined mesh.
- The error is recomputed, and the iterative
process (solve — error analysis — adaptive refinement) repeats until
the convergence criteria are satisfied or the maximum number of adaptive
passes is completed.
- If a frequency sweep is being performed, then the problem is solved at the other frequency points without further refining the mesh. An adaptive solution is performed only at the specified solution frequency.
Note:
An initial mesh is not generated each time it starts the solution process. The initial mesh is generated only if a current mesh is unavailable.
