AEDT Virtual Desktop
The Ansys Electronics Desktop virtual desktop experience is summarized in the following steps:
Create a virtual desktop. A project space administrator creates a virtual desktop with Ansys Electronics Desktop installed. See Creating a Virtual Desktop in the Administration Guide.
Important notes for Ansys Electronics Desktop:
Operating system: Windows Server 2022
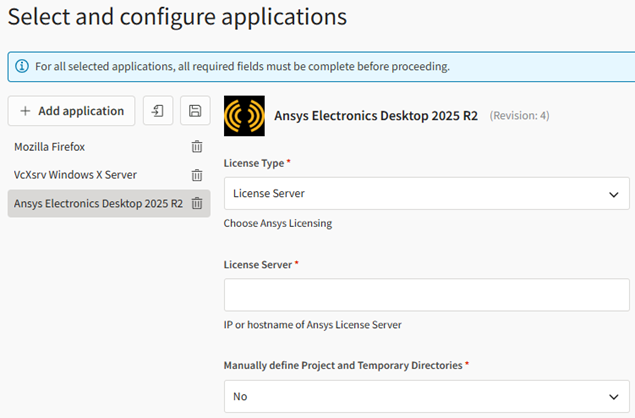
Applications: Select Ansys Electronics Desktop. Mozilla Firefox and VcXsrv Windows X Server are added automatically.
Ansys recommends adding Notepad++ as well.
To configure the application, select the Ansys Electronics Desktop application in the left pane and specify configuration settings in the right pane.
 Note: Ansys recommends that you create the virtual desktop without any applications, and then add the application after the virtual desktop has been created. See Adding Applications to a Virtual Desktop in the User's Guide. Sometimes, Windows updates are triggered on newly created virtual machines, causing application installation to fail.
Note: Ansys recommends that you create the virtual desktop without any applications, and then add the application after the virtual desktop has been created. See Adding Applications to a Virtual Desktop in the User's Guide. Sometimes, Windows updates are triggered on newly created virtual machines, causing application installation to fail.Hardware: c5d, c6i, m5d, m6i, m6id, hpc6a, hpc6id, g4dn, g3
When solvers are used and hardware-accelerated graphics are not needed, c5d and m5d instances are recommended.
For accelerated graphics or GPU compute, g3 and g4dn instance types are recommended. In the GPU driver options, GRID drivers are recommended for accelerated graphics, while GRID or Tesla drivers can be used for GPU compute.
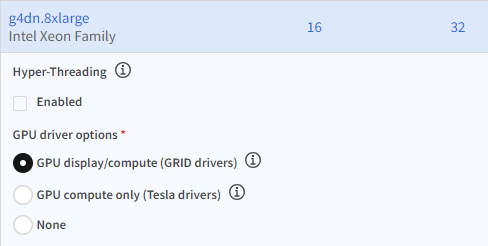
For information about GPU driver options, see NVIDIA GPU Driver Support.
Launch a virtual desktop session. Users with access to the project space connect to the virtual desktop to start a virtual desktop session. See Launching a Virtual Desktop Session in the User's Guide.
Run the remote application. Once the desktop is open you can run simulations on the virtual desktop just as you would on your local desktop. For information about AEDT, refer to the Ansys Electronics Documentation.
If you need to transfer files to the virtual desktop, see General Guidelines for Transferring Files in the User's Guide.


