This release of Ansys HPC Platform Services offers the following new features and enhancements:
Improved User Experience
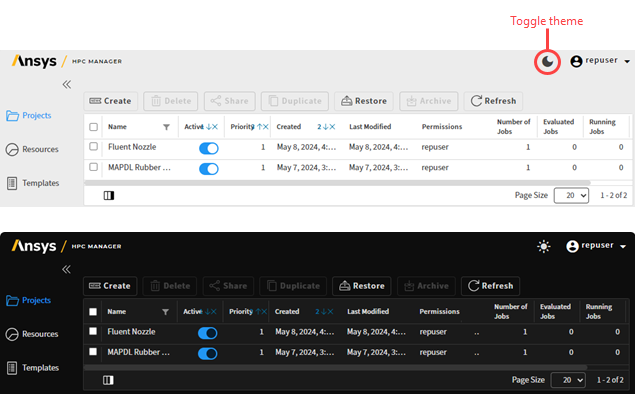
To reflect its full capabilities, the Ansys HPC Job Manager web app has been renamed Ansys HPC Manager.
Styling updates to the Ansys HPC Manager interface provide a fresh, modern look and feel that is consistent with the new design language defined for Ansys software.
You can now choose to display the Ansys HPC Manager interface using a Dark or Light theme according to your personal preference.
2024 R1 and 2024 R2 Templates
Release 2024 R1 and 2024 R2 templates have been added for Ansys Fluent, Mechanical, and LS-DYNA.
More Application Settings
When defining applications in a resource configuration, additional settings are now available:
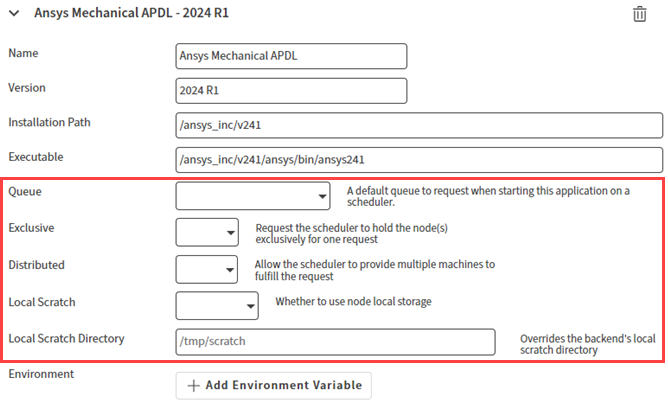
Multi-Node Local Scratch
When defining a job definition, application settings, or compute resource properties, a Local Scratch option lets you specify whether to use a scratch directory local to the compute node(s) as the job execution working directory.
Using a local scratch directory may optimize performance if the solver has heavy Input/Output (I/O) patterns (for example, produces numerous, relatively large files, re-reads the same file multiple times, or continuously opens and closes files).
You can override the default scratch directory if desired by specifying the path of an alternate directory in the Local Scratch Directory field.
More Job Scheduler Options
When defining resource requirements in a task definition template or job definition, you can optionally select a specific Compute Resource for the job. This can be a cluster or an evaluator.
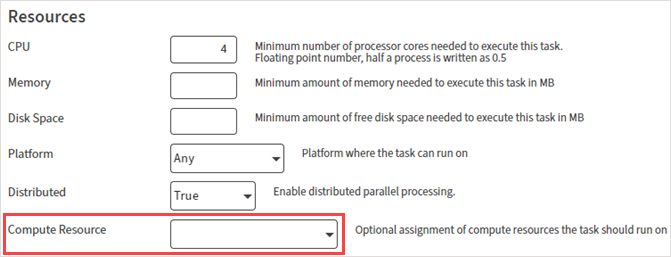
This option is also available from the API.
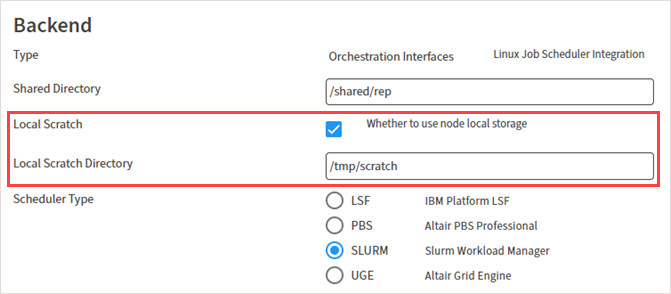
When defining HPC resource requirements for a cluster, the following new options are available:
Queue. A default queue for job submission. Select a queue from the drop-down or type the queue name.
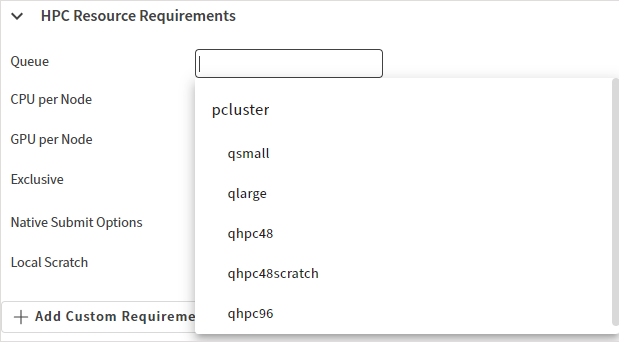
Native Submit Options. Additional command line options to pass directly to the scheduler.
Local Scratch. Whether to use a local scratch directory on compute nodes when the solution is running.
Custom Task Commands
Custom commands such as Interrupt can be defined in a solver execution script via the Job Management Service (JMS) API.
When commands are added to the script, they are displayed in a Queue Command drop-down when viewing a job's tasks in Ansys HPC Manager.
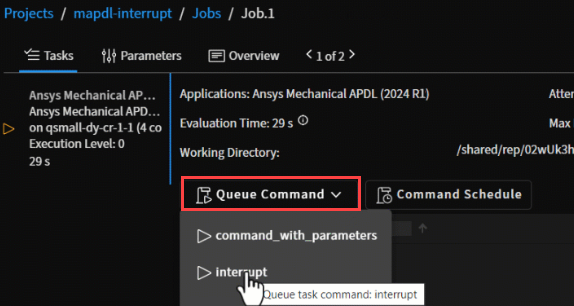
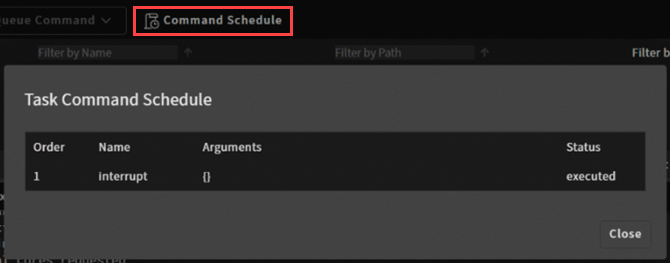
When a command is selected and queued, it is added to the task's command schedule. To view a list of queued commands and their status, click the Command Schedule button.
Multiple Jobs on the Same Node
To optimize design point runs, which have numerous small jobs, multiple jobs can be scheduled to run on the same node.
This works when the Distributed property is set to False and Max Num Parallel Tasks is set to N.
When a job is submitted, a Cores*Max Num Parallel Tasks
calculation is performed to determine the number of cores to request from the
orchestrator.
Improved Observability and Monitoring
The job details view now includes a scaling indicator to provide insight into job orchestration.
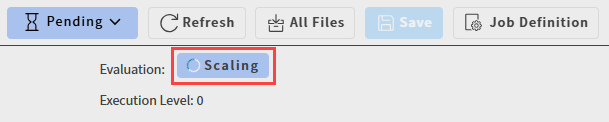
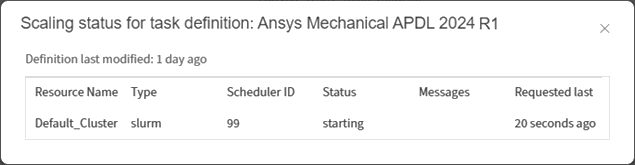
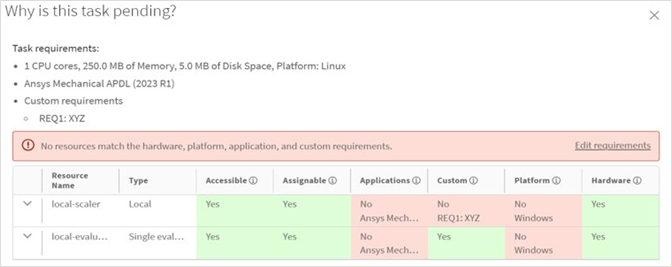
When analyzing a Pending task to see why it is still pending, autoscaling agents are now considered. Previously, only evaluators were considered.
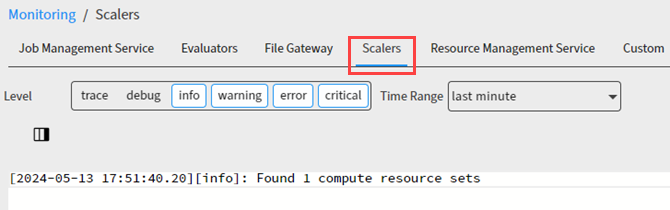
On the page, a new Scalers tab is available.
API Enhancements
The methodology used to asses why a job is pending has been moved to the Resource Management Service (RMS) with an API that can be queried by any client (web application, desktop, and so on).
This method was updated to consider scalers (autoscaling agents) in addition to evaluators. These changes have been incorporated into the Ansys HPC Manager web app (as described in Improved Observability and Monitoring).
From an API perspective, this will allow clients to ask questions prior to job submission to determine whether a job can run.
As described in Custom Task Commands, the API in the Job Management Service (JMS) enables you to define custom command behavior for a task. Custom commands are made available in the Ansys HPC Manager web app via a Queue Command drop-down on the job view page.

