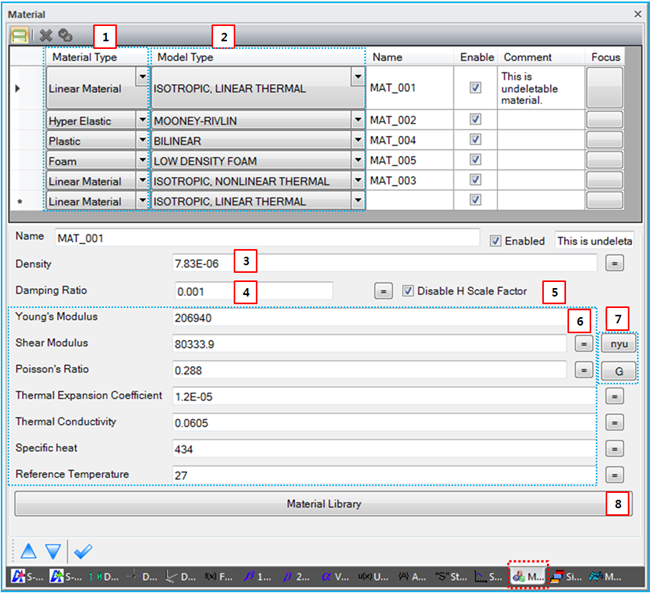
As shown in the figure below, properties such as Name, Material Type, Model Type, Sign and so on can be defined in the Material sub-entity window. General Sub-Entity Properties have been introduced in Figure 8.18: General properties of sub-entity pages and toolbar and the special properties are shown in the table below.
Figure 8.78: Common properties for Material
| Parameter | Symbol | Description | Dimension (Range) |
| 1. Material Type | N/A | Use to set one of materials in the Figure 8.76: Material type table. | N/A |
| 2. Model Type | N/A | Use to set one of models in the Figure 8.76: Material type table. The formulations are introduced in each material property. | N/A |
| 3. Density |
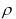 | Use to set the density of the material. This determines the mass and mass moment of inertia of the body in Equation 8–72 and Equation 8–73. |
Mass /Length^3 (Real≥0) |
| 4. Damping Ratio |
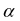 |
Use to set the stiffness-proportional damping ratio for nodal flexible and EasyFlex bodies. The damping matrix of an element can be defined as follows.
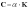
where |
N/A (Real≥0) |
| 5. Disable H Scale Factor |
 |
Use to set the variable dependent on the step size for the damping matrix as follows.
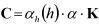
When this option is not selected, the variable is internally defined in the Motion solver and the damping matrix is determined by the above equation. When this option is selected, the variable is set to one. Since this option is only available for beam and shell elements, the variable for solid elements and EasyFlex elements is always set to one. | N/A |
| 6. Parameters | N/A | Use to define parameters for each material model. The parameters are introduced in Formulation and Parameters for a Linear Material. | N/A |
| 7. Calculators | N/A | Use to calculate Poisson’s Ratio or Shear Modulus. When the
 button is
clicked, Poisson's Ratio is calculated in Hooke's law with the
defined Shear Modulus. When the button is
clicked, Poisson's Ratio is calculated in Hooke's law with the
defined Shear Modulus. When the  button is clicked, Shear
Modulus is calculated in Hooke's law with the defined Poisson's
Ratio. button is clicked, Shear
Modulus is calculated in Hooke's law with the defined Poisson's
Ratio. | N/A |
| 8. Material Library | N/A |
Use to open the material library dialog as shown in the figure below.
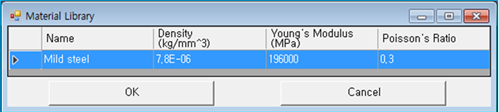
One of the available materials can be selected. When you click in the material library dialog, the properties of the selected material are automatically set in the specified material. If you want to add or remove a material property in the material library dialog, see Material Library. | N/A |
Remarks
After creating a material entity, its Material Type and Model Type cannot be changed to another type.