A nonlinear static analysis is performed setting the Newton-Raphson option to in Analysis Settings.
The at rest stress state is calculated using a single substep as shown below.
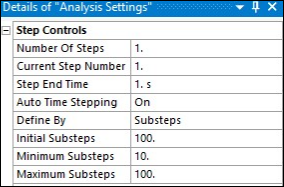
The active and passive pressure-state loads are applied via 10 initial and 100 maximum substeps with automatic time-stepping enabled.
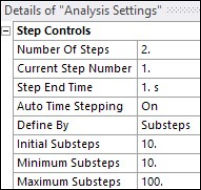
Calculating the at rest stress state in the first load step results in vertical displacements:
Generally, the soil exists in an already consolidated state. Initial displacements due to at-rest loads are therefore unnatural and should be minimized.
The vertical stress state varies linearly with the depth of the soil, expressed as:
where:
|
|
|
|
|
|
The coefficient of lateral earth pressure is the ratio of horizontal to vertical
stress components. For a horizontally retained non-overconsolidated soil under
elastic loading conditions, it is defined (via Poisson’s ratio
) as:
so that the horizontal stress components can be calculated as [2]:


