VM-AM-MECH-006
VM-AM-MECH-006
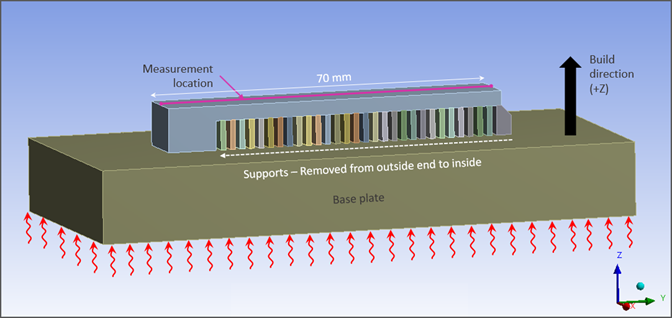
Additive Manufacture of 70-mm Cantilever with Supports Using Inconel 625
Overview
| Reference: | Model and experimental results courtesy of Renishaw plc |
| Material: | Inconel 625 |
| Solver(s): | Additive in Mechanical |
| Physics/Modes: | Linked Transient Thermal - Static Structural |
| Supports Included: | Yes |
| Platform: | Windows only |
Test Case
Perform a simulation of a Laser Powder Bed Fusion (L-PBF) additive manufacturing process of a 70-mm cantilever beam with supports printed with Inconel 625 nickel chromium alloy.
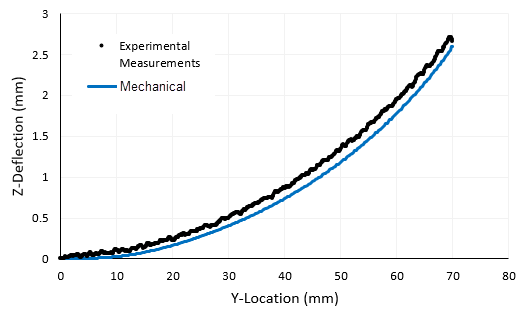
Find the Z-direction distortion along the top edge of the part after the supports have been removed and compare results to measurements taken of the built part.
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
Ansys predefined material properties are used for Inconel 625 from the Additive Manufacturing Materials library. The simulation includes a build step, a cooldown step, and support-removal steps.
Heat is applied at a constant temperature (100°C) to the underside of the base plate during the build step. Room-temperature convection is applied to that same surface during the cooldown step.
Throughout the simulation, the base plate is anchored by a fixed boundary condition on the underside of the plate.
Supports are removed from the outside end to the inside.
Deflection results are measured along the centerline of the top surface after the supports were removed. For comparison purposes, the minimum deformation is set to zero for both the experimental and simulation data.
The analysis is performed using a Cartesian mesh.
| Build Settings | Build Conditions | Cooldown Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Deposition/Powder Layer Thickness = 0.03 mm | Preheat Temperature = 80°C | Room Temperature = 22°C |
| Hatch Spacing = 0.1 mm | Gas Temperature = 80°C | Gas Temperature = 22°C |
| Scan Speed = 1000 mm/sec | Powder Temperature = 80°C | Powder Temperature = 22°C |
| Dwell Time = 10 sec | Gas Convection Coeff = 0.00001 W/mm2°C | Gas Convection Coeff = 0.00001 W/mm2°C |
| Dwell Time Multiple = 1 | Powder Convection Coeff = 0.00001 W/mm2°C | Powder Convection Coeff = 0.00001 W/mm2°C |
| Number of heat sources = 1 | Powder Property Factor = 0.01 | Powder Property factor = 0.01 |
| Mesh and Material Settings |
|---|
| Element size = 0.25 mm Cartesian mesh |
| Projection Factor = 0.7 |