You can specify the minimum number of element layers created in regions that constitute "gaps" in the model for proximity-based sizing. For the purposes of specifying proximity-based sizing, a "gap" is defined in one of two ways:
The internal volumetric region between two faces
The area between two opposing boundary edges of a face
Proximity-based sizing is defined by the following properties:
The Proximity Gap Factor is the number of layers of elements to be generated in the gaps. Proximity Size Function Sources determines which regions of proximity are considered in calculations.
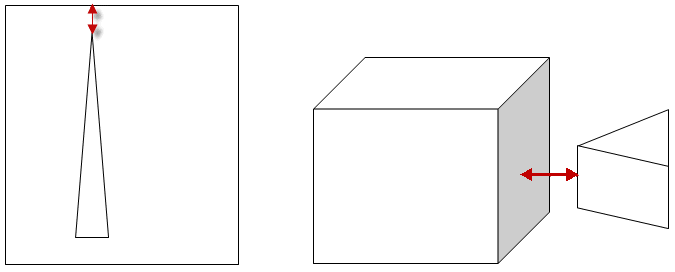
Note: The proximity sizing does not recognize the proximity between certain entities in cases involving voids in a model. For example, the proximity between a vertex and an edge on a face in 2D (below left) is ignored if the triangle is a void in the rectangle. Similarly, the proximity between a vertex or edge and a face in 3D (below right) is ignored if the prism and the block are voids in a larger domain. The two-headed arrows in the figure indicate the areas where proximity is ignored.