Both DRG and DRGEP stop the reduction process when the induced error on targeted parameters goes beyond the user-specified tolerance level during removal of species from the full mechanism. In some cases, the induced error dramatically increases when a group of species is removed from the full mechanism. Within this group, only a few species are responsible for the noticeable amount of error on the targeted parameters, while the rest could have been safely removed. However, because DRG and DRGEP remove such a group of species simultaneously, the species that lead to significant amounts of induced error and the ones leading to induced error within the tolerance level cannot be treated separately. Therefore DRG/ DRGEP cannot generate the smallest skeletal mechanism possible without additional steps to treat these two types of species separately.
A species sensitivity analysis implemented in the Reaction Workbench allows DRG/ DRGEP to differentiate between species in such a group, in terms of their effect on error. This sensitivity analysis is performed in the following steps:
After DRG/DRGEP has generated the smallest skeletal mechanism that meets the error criteria, use DRG/DRGEP to identify the pool of candidate species that might be removed from this skeletal mechanism without pushing the induced error on target parameters beyond the user-specified tolerance level. This is accomplished by increasing the internal threshold of DRG/ DRGEP so that the resulting skeletal mechanism would produce an induced error that is beyond the tolerance level.
Remove each candidate species individually from the smallest acceptable skeletal mechanism generated by DRG/DRGEP and calculate the induced error on target parameters for this species.
Rank the candidate species using their induced error in ascending order.
Remove candidate species from the smallest skeletal mechanism generated by DRG/DRGEP in the order prescribed in step 3 and calculate the cumulative induced error on target parameters after each species is removed. Stop the process when the cumulative induced error is beyond the tolerance level specified by the user.
Because the project used to cover the desired range of conditions has to be run to calculate the induced error on target parameters, steps 2 and 4 in the sensitivity analysis can be time-consuming. We also note that the number of species removed by the sensitivity analysis is variable, ranging from a few species to 20%–30% of the species in the skeletal mechanism generated by DRG/DRGEP. Nonetheless, we find this option to be a good addition to the mechanism-reduction suite, providing significantly smaller mechanisms in many cases.
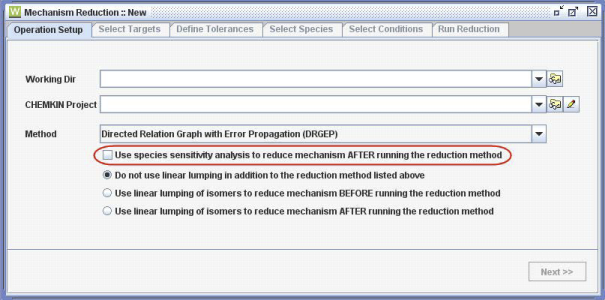
The species sensitivity analysis has been implemented in Reaction Workbench for both DRG and DRGEP methods, as shown in Figure 3.1: Selecting sensitivity analysis for DRGEP in the Reaction Workbench . The check-box enables the sensitivity analysis to be performed after DRG or DRGEP has generated the smallest skeletal mechanism. The entire process is run automatically by the Reaction Workbench. If a method other than DRG or DRGEP has been selected, the check-box for the species sensitivity analysis is disabled in the Reaction Workbench User Interface.