For a Generalized Newtonian sub-task (isothermal or not), you can assign multiple materials to inflow boundaries for a polymer flow simulation, providing an alternative approach to defining coextrusion problems.
The multiple-materials approach lets you define several materials and their specific properties. You then only need to specify which single material enters through each inflow boundary, with the condition that the fluid(s) are entering the flow domain only by inflow boundaries. Additional conditions are described in Conditions and Limitations for Using Multiple Materials.
The inputs directly related to using multiple materials are provided in this section. You will need to set up the rest of the problem (sub-tasks, boundaries, and so on) as usual.
To model flows using multiple materials, such as coextrusion, perform the following:
Create a new task (either steady, transient, or evolution).
 Steady-state problem(s)
Steady-state problem(s)
 Time-dependent problem(s)
Time-dependent problem(s)
 Evolution problem(s)
Evolution problem(s)
Specify the domain of the sub-task.
 Domain of the sub-task
Domain of the sub-task
Modify the default material data for the sub-task.
 Material data
Material data
You can specify the material properties such as shear-rate dependence of viscosity, density, inertia, or gravity.
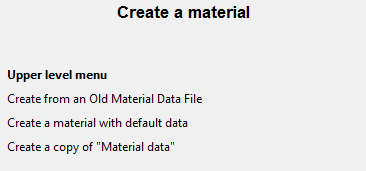
Create additional materials as needed.
 Create a material
Create a materialSelect Create from an Old Material Data File to create the material using previous data from a file. You are prompted to browse for an appropriate materials file (*.mat).
Select Create a material with default data, to create the material (for example Material Data #2) using default settings.
Select Create a copy of "Material data" to create the material using the settings of the current problem’s material data.
Note: The listing changes to show as many materials that have already been created.
Set the material data for each material that you want to include with the problem. For each material, you can specify the material properties such as shear-rate dependence of viscosity, density, inertia, or gravity.
Specify inflow boundaries (Inflow Calculation for Generalized Newtonian Flow).
In the Flow boundary conditions panel, select the boundary that represents the inflow and click Modify.
 Flow boundary conditions
Flow boundary conditions
Select Inflow as the boundary type.
 Inflow
Inflow
In the Inflow calculation panel, specify inflow properties as you normally would, such a flow rate.
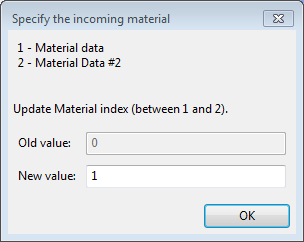
In the Inflow calculation panel, assign a material for the inflow boundary.
 Modify incoming material
Modify incoming material
Note: Modifying incoming materials is available only for inflow boundaries.
In the Specify the incoming material panel, select the material data option that best suits your requirements for this particular inflow boundary.
Repeat as needed for as many inflow boundaries as you require. Assign different materials to each inflow boundary to model coextrusion of those materials throughout the domain.
In the Numerical parameters menu, enable the convergence strategy for multiple-materials.
 Enable convergence strategy for multiple-material flows
Enable convergence strategy for multiple-material flows
You can also enable or disable this convergence criteria in the Save & Exit menu within Ansys Polydata.
Note: Small distortions may appear when displaying fluid fraction results:
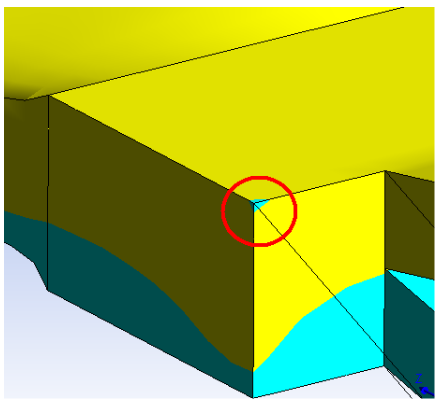
This can be remedied by editing the Modify the fluid fraction diffusivity explicitly in the Advanced options for the Interpolation menu.
![]() Interpolation
Interpolation