Genetic aggregation is a metamodeling technique that automatically selects the best metamodels, including building aggregations of different surrogates.
To select the best metamodel, Genetic Aggregation uses a genetic algorithm that generates populations of different metamodel solved in parallel. The fitness function of each metamodel is used to determine which one yields the best approach. It takes into account both the accuracy of the metamodel on the design points and the stability of the metamodel (cross-validation).
The Genetic Aggregation response surface (GARS) can be a single metamodel or a combination of several different metamodels (obtained by a crossover operation during the genetic algorithm).
Advanced Settings
You can access the GARS advanced settings in the MOP settings dialog box.
Right-click the MOP node and select from the context menu.
Select the Use advanced settings check box.
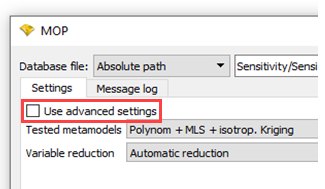
In the Advanced Settings tab, under Genetic Aggregation Response Surface, select the Use check box.
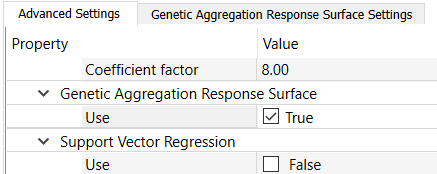
Switch to the Genetic Aggregation Response Surface Settings tab.
Click .
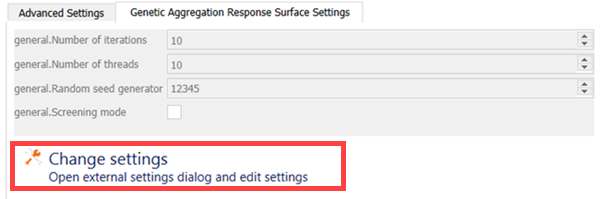
Change the settings as required.
Name Default value Description Number of iterations 10 Advanced option determining the maximum allowable number of iterations of the genetic algorithm. If Screening mode is True, Number of iterations is ignored. Random seed generator 12345 Advanced option allowing you to specify the value used to initialize the random number generator.
By changing this value, you start the Genetic Aggregation from a different population of response surfaces.
Screening mode False Replace the genetic algorithm by a unique sampling of response surfaces. Number of threads 10 Advanced option determining the number of threads to use in parallel to solve Genetic Aggregation. To save and close the dialog, click .
Supported Versions
The following versions of GARS metamodel are supported and tested: 2021 R2 and later.


