The primary objective of oSP3D is to extend optiSLang's capabilities to distributed data like FEM mesh data (3D) or signals (1D and 2D). With oSP3D, you can visualize various statistical properties, analyze and expand random fields, simulate random structural designs, and much more.
oSP3D Algorithms
oSP3D provides algorithms for:
Real-time approximations of 3D, 2D, and 1D field data
Free-form shape optimization
Automatic parametrization of spatial variations based on virtual or real experiments
Mesh morphing for the creation of new random designs
Analysis of random properties of structures by inspecting statistics on the structure
Detection of hot spots at potential failure locations, sensor positions, and so on
Random field modeling
Analysis of measurements such as STL and photos
oSP3D algorithms can be grouped as follows:
Statistical hot spot detection
For data-based ROMs, sensitivity analysis and approximation with field-MOPs
Random fields based on measurements
Random fields based on autocorrelation models
oSP3D Software Features
The following software features support your multi-dimensional data analysis:
Ansys Mechanical plugin for geometric imperfections and result export
GUI for import, export, analysis, and visualization
Standalone oSP3D 3D viewer
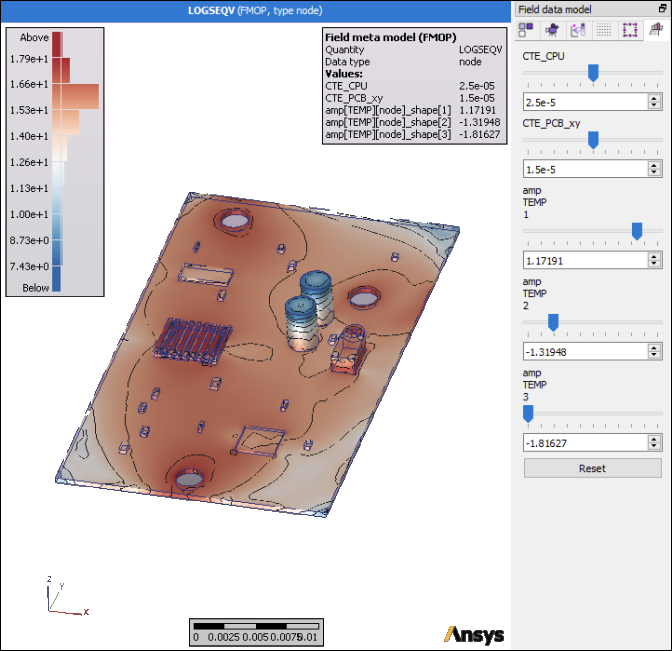
Interactive visualization with sliders for meta models
Display changes of geometry and their effect on component behavior
Embedded scripting (Lua) for very fast loops on large data sets
Binary interfaces to field-MOP (DLL)
Several CAE interfaces (ANSYS, ABAQUS, LS-DYNA, NASTRAN, STL, PNG, and more)
For your convenience, the next few topics define oSP3D terms, abbreviations, and acronyms and provide a proven path for learning how to use oSP3D.


