The domain of the 3D Multi Material Euler (MME) solver can be filled with material and initial conditions using a closed single connected surface body. The interior of the closed surface body inside the Eulerian domain will be filled with the material and initial conditions of that surface body.
A surface body is defined as a 3D (virtual) Euler body, when the Reference Frame of that surface body is switched in the setting from Lagrange to Eulerian (Virtual).
Not only does this definition trigger the creation of the virtual MME domain, but the interior volume of the closed surface body is used to fill the virtual MME domain with the material and initial condition assigned to it.
The surface must be single connected. This means that the surface consists of faces which only connect a maximum of two faces along their edges, and no T-joints or multiple joints are allowed.
Note: The thickness of the Eulerian surface body is not taken into account to compute the internal filling volume. However, it needs to have a non-zero thickness value assigned.
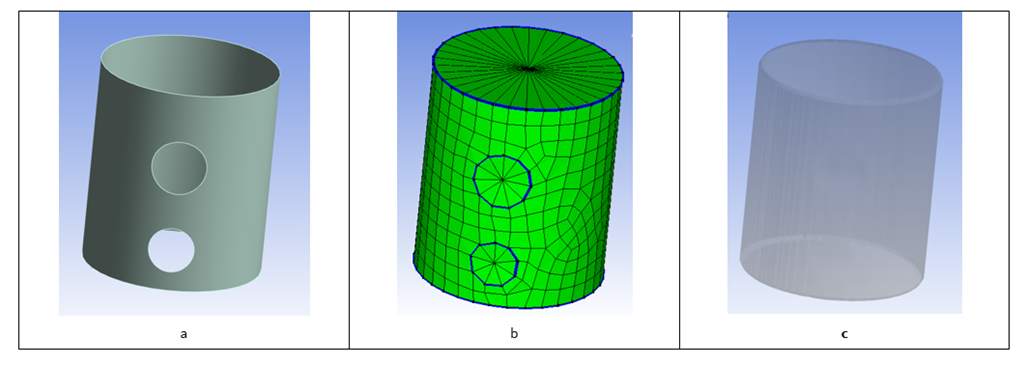
The closed single connected surface, that is used to map material and initial conditions into the MME domain, may contain holes or openings. The mapping algorithm will generate a completely closed Euler surface body by closing the holes and openings with triangular elements. The triangular elements are generated from the nodes along the edge of a hole or opening and a central node in the middle of the hole or opening, that has the average x-, y-, and z-coordinate of all nodes along the edges of the hole or opening.
Figure 21.1: Example of (a) Euler Surface with Holes and Openings, (b) Closing of Holes and Openings in Euler Surface, and (c) Resulting Material Mapping into MME Euler Domain