VM-LSDYNA-SOLVE-001
VM-LSDYNA-SOLVE-001
Steady State Thermal Analysis of 3D Hollow Spheres with Convection Boundary
Condition
Overview
| Reference: | Kreith, F. (1959). Principles of Heat Transfer (2nd ed.). International Textbook Co. |
| Analysis Type(s): | Steady State Thermal |
| Element Type(s): | Solid |
| Input Files: | Link to Input Files Download Page |
Test Case
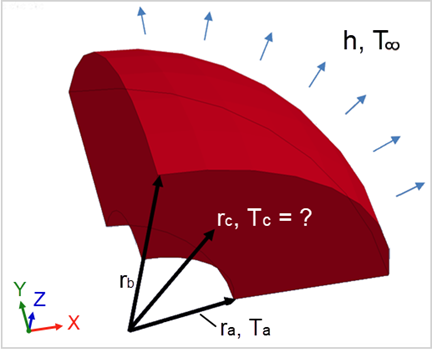
A hollow sphere with an inner radius ra and an outer radious rb has an inner surface temp of 100°C. The material of the hollow sphere is isotropic. A convective boundary condition is applied at the outer surface rb. The external ambient temperature T∞ is 0°C, and the convective heat transfer coefficient h is 1 W/(m2°C). Compute the Steady state temperature at rc = 3.51419 m.
| Material Properties | Geometric Properties | Loading |
|---|---|---|
| k = 1 W/(m°C) | ra = 2 m | Ta = 100°C |
| h = 1 W/(m2°C) | rb = 5.02839 m | T∞ = 0°C |
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
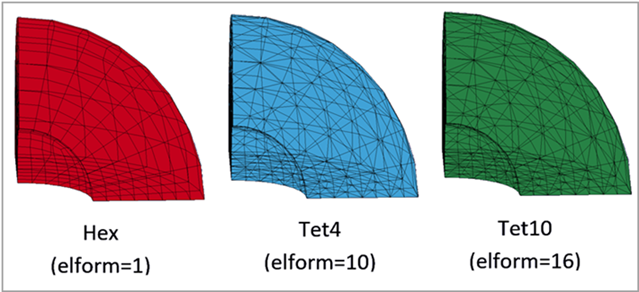
LS-DYNA Thermal Solver 11 is used for this example. Three hollow spheres are modeled using ELFORM = 1, 4, 16. The temperature and convection boundary conditions are applied using the keywords *BOUNDARY_TEMPERATURE and *BOUNDARY_CONVECTION respectively. One eighth symmetry is used, and the heat flow is limited to the radial direction only.
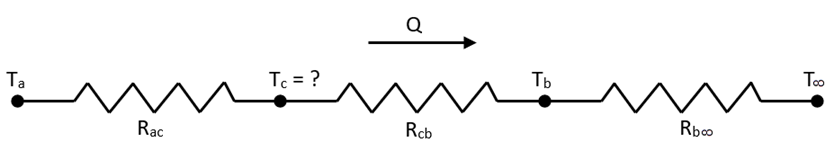
At steady state, the rate of heat dissipation Q is
where the thermal resistances Rac, Rcb, and Rb∞ can be expressed as follows:
From the above equations, the analytical solution to Tc is 36.7617°C.