VM-LSDYNA-WB-008
VM-LSDYNA-WB-008
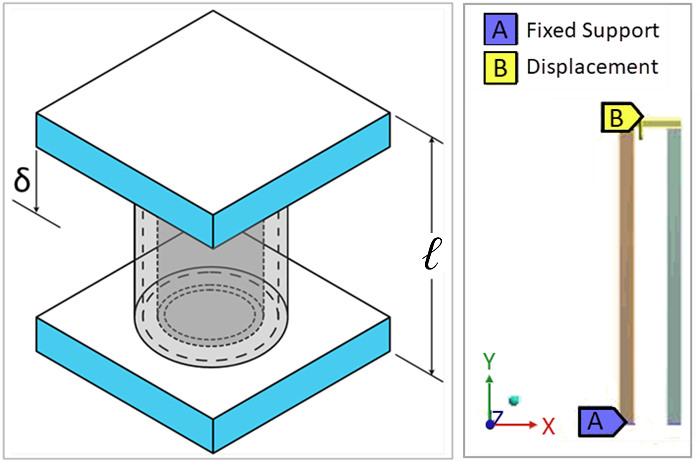
Plastic Compression of a Pipe Assembly
Test Case
There are two coaxial tubes. The inner one is made of 1020 CR steel and has a cross-sectional
area As. The outer tube is made of 2024-T4 aluminum alloy and has a cross-sectional area Aa.
They are compressed between heavy, flat end plates, as shown in the problem sketch. Determine
the load-deflection curve of the assembly as it is compressed into the plastic region by an
axial displacement.
This test case is also solved using Ansys Mechanical. See VM-WB-MECH-047.
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
Assume that the end plates are so stiff that both tubes are shortened by exactly the same
amount. Because the geometry and loading are symmetric about the y-axis, the above problem can
be analyzed as an axisymmetric problem.