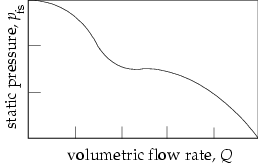
The relationship between volumetric flow rate and the pressure drop across the fan (static pressure) is described by the fan characteristic curve, which is usually supplied by the fan manufacturer. Figure 21.10: Tube-axial Fan Curve shows a characteristic curve for a common tube-axial fan. The total volumetric flow rate, Q, is plotted against fan static pressure, pfs.
For a linear fan characteristic curve, only the volume flow rate at zero static pressure, Q0 , and the fan static pressure at zero flow rate, p0 , need to be specified. The equation for a linear fan characteristic curve is
(21–5) |
In most cases, the linear characteristic curve does not adequately approximate the true fan characteristic curve over its entire operational range, so it is best to specify the actual fan curve, if possible.
Fan static pressure is computed by:
(21–6) |
where pintake is the pressure averaged over the face of the intake side of the fan, and pdischarge is the pressure averaged over the face of the discharge side of the fan.
For internal fans, both pintake and pdischarge are computed by Ansys Icepak. For an intake fan, pdischarge is computed by Ansys Icepak and pintake is the ambient pressure. The value of the ambient pressure is specified under Ambient conditions in the Basic parameters panel (see Ambient Values). For an exhaust fan, pdischarge is the ambient pressure, and pintake is computed by Ansys Icepak. The default ambient pressure is zero (gauge pressure) and this should be satisfactory in almost all situations.
The accuracy of the fan flow rate used by Ansys Icepak is directly related to the accuracy with which the fan static pressure is computed. This, in turn, depends on how accurately pressure losses in the entire system are modeled. Therefore, care should be taken to model all features of the system that contribute to the overall nature of the pressure distribution in the system.
You can create a report of the fan operating point (pressure rise and volume flow rate) for a characteristic curve fan, as described in Fan Operating Points Report.