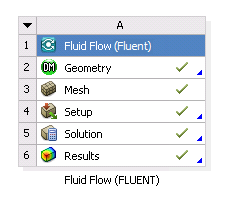
This example describes when the files that are generated and used by Fluent are written and how the cell states change as you work with a Fluent-based system in Workbench.
Add a new Fluid Flow (Fluent) analysis system to the Project Schematic. The state of the Geometry cell is Attention Required and that the states for the Mesh, Setup, Solution, and Results cells are Unfulfilled.
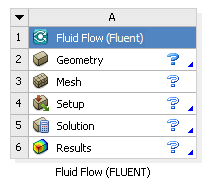
Import a geometry file by using the context menu on the Geometry cell. The state of the Geometry cell becomes Up-to-Date and the state of the Mesh cell becomes Refresh Required.
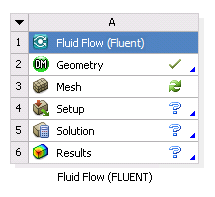
Double-click the Mesh cell. The Ansys Meshing application launches and loads the geometry file. The state of the Mesh cell becomes Update Required.
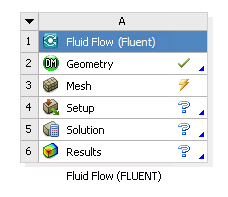
In the Ansys Meshing application, specify settings for the mesh, then select the Update command. The mesh is generated, the mesh (
.msh) file is written, the state of the Mesh cell becomes Up-to-Date, and the state of the Setup cell becomes Refresh Required.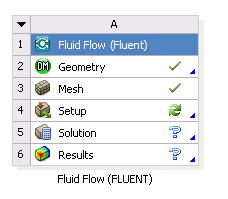
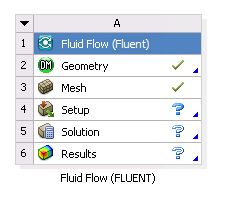
Double-click the Setup cell. Fluent launches and loads the mesh file. The state of the Setup cell becomes Attention Required.
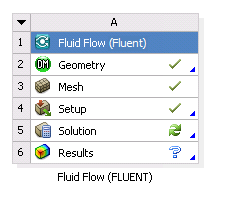
In Fluent, specify boundary conditions, initialize the solution, and enter a nonzero number of iterations on the Run Calculation task page. The state of the Setup cell becomes Up-to-Date, and the state of the Solution cell becomes Refresh Required.
In the Fluent application, select the Calculate button. The settings (
.set) file is written and iterations begin. The state of the Solution cell becomes Update Required.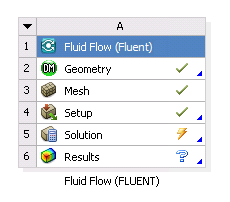
Iterations are completed, or the solution meets the convergence criteria. The state of the Solution cell becomes Up-to-Date and the state of the Results cell becomes Refresh Required.
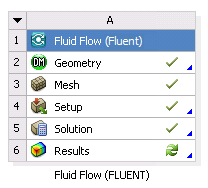
Double-click the Results cell. CFD-Post launches.
The case (
.cas.h5) and data (.dat.h5) files are written, CFD-Post loads the case and data files, and the state of the Results cell becomes Up-to-Date.