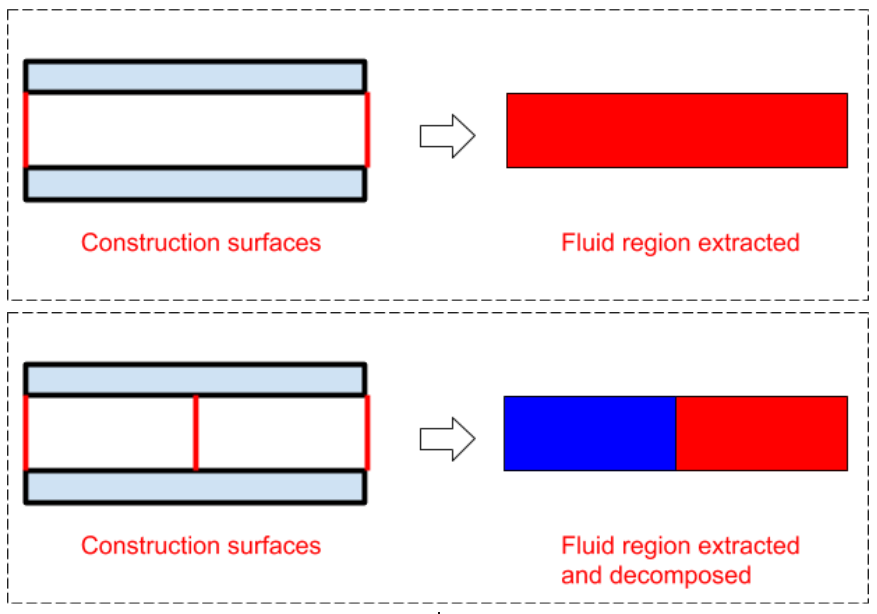
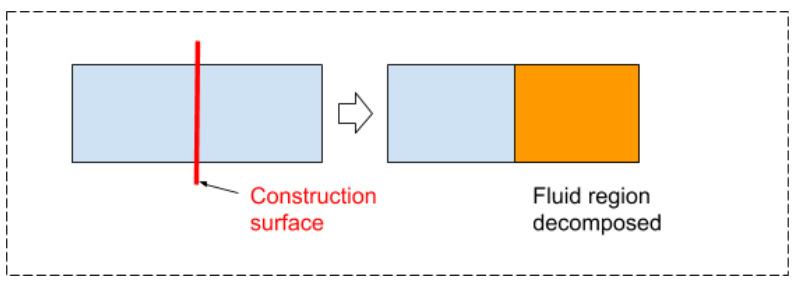
For geometries that have primitive construction surfaces (for example, capping surfaces, or cylindrical surfaces for moving reference frames) already defined as part of the CAD model, you can use the Identify Construction Surface task to locate those portions of the geometry and identify them as such so that Fluent can handle them accordingly during the meshing process. These surfaces are used to further decompose the main fluid into multiple regions, such as regions around a rotating fan for a moving reference frame (MRF) simulation.
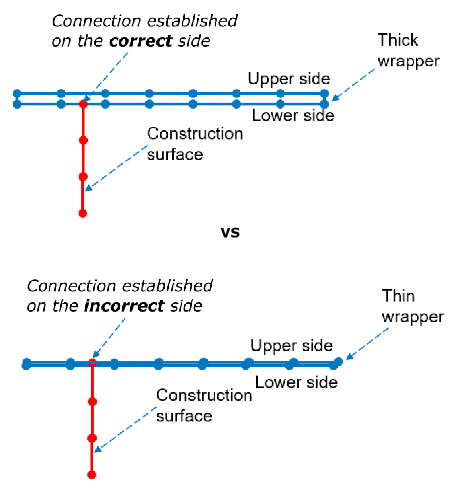
Note: The workflow cannot properly connect construction surfaces to wrapped regions that are too thin.
Specify a Name for the construction surface, or use the default name (
construction-surface-1).For Method, choose from the following:
Select Existing if the construction surface is already defined as part of your imported geometry.
Select Box if the construction surface is to be defined using a bounding box.
Select Offset Surface if the construction surface will be offset from the surface of an existing, selected object or zone.
When the Method is set to Existing, you can then select a single label, object, or zone in the corresponding list.
When the Method is set to Box, you can set the Coordinate Specification Method to the following options:
Use the Ratio relative to geometry size option so that you can define the construction surface based on the relative size of selected object(s) or zone(s). Choose whether to Select By the object, label, or zone name in the corresponding list.
Use the Directly specify coordinates option so that you can explicitly define the location and dimension of the construction surface without having to select object(s) or zone(s).
In addition, under Box Parameters, additional settings are required.
When you select Ratio relative to geometry size as the specification method, the Box Parameters hold the minimum and maximum extension ratios for the X, Y, and Z dimensions. By default, they are set to extend the dimensions of a bounding box around your selected object(s) or zone(s) out by a factor equivalent to the total singular length of the geometry in the X, Y, and Z directions. You can change the values according to your needs, and the display in the graphics window will change accordingly.
When you select Directly specify coordinates as the specification method, the Box Parameters hold the minimum and maximum extension distance for the X, Y, and Z dimensions. By default, they are set to values that correspond to the extension ratios, but you can set them to more suitable values as required, and the display in the graphics window will change accordingly.
When the Method is set to Offset Surface:
Select one or more items in the list of pre-existing objects.
Specify a value for the Defeaturing Size, or use the default setting. This will obtain the rough shape of the selected object(s), which are wrapped using this size.
Specify a value for the Height of the offset construction surface, or keep the default setting. This is how far from the selected object(s) the rough shape is offset.
Once your selections are made, click Identify Construction Surface and proceed onto the next task.
If you need to make adjustments to any of your settings in this task, click Revert and Edit, make your changes and click Update, or click Cancel to cancel your changes.
Note: You can directly select items in the lists or you can use the Filter Text option in the drop-down to provide text and/or regular expressions in filtering the list (for example, using *, ?, and []). When applicable, you can also choose the Use Wildcard option in the drop-down to provide wildcard expressions in filtering the list. When you use either
?or*in your expression, the matching list item(s) are automatically selected in the list. Use^,|, and&in your expression to indicate boolean operations for NOT, OR, and AND, respectively. See Filtering Lists and Using Wildcards for more information.


