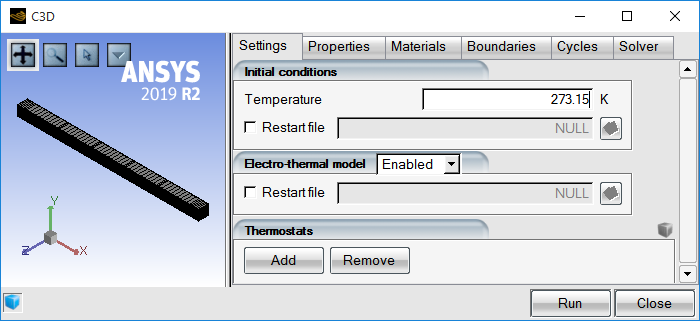
The initial settings for C3D affect the initial temperature and thermostat identifiers and positions, if they are activated in the simulation.
Enter the initial temperature for the solid domain.
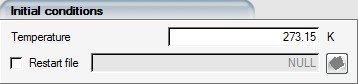
This temperature will be applied throughout the domain, for all the materials.
If a restart file is specified, the solution is initialized from the solution read from the file. This option can be used to restart a computation or to continue a computation with different settings.
The Electro-thermal model can be used to evaluate the resulting Joule-Thomson heating effects of an electrical current carrying conductor. The electrical problem can be described by Maxwells continuity equation that calculates the electric potential in a material:
The electrical problem is described by Maxwell’s continuity equation, which determines the electric potential in a material:
where:
: Voltage potential [Volts]
: Temperature dependent electrical conductivity [S/m]
: Charge density [C/m3]
: Induced electro-motive force caused by a temperature gradient
(Seebeck effect)
The heat produced electrical conduction can be described by the Joule-Thomson effect. The electric potential gradient is used to calculate the heat generated per unit volume:
where:
: Peltier Coefficient
: Current Density Vector
The Peltier coefficient can be related to Seebeck coefficient, s, by temperature:
The equation can be then recast as:
The first term on the right corresponds to Joule heating and
the second term includes both Peltier effects at a junction between two different conductors, and
Thomson effects,
due to the thermal gradient within a conductor.
Boundary conditions in terms of voltage can be specified at the terminals of an electrical conductor:
where and
are the voltage potential defined at the two ends of the
conducting material. Neumann conditions for the current
in the material are usually not specified but are computed from
the voltage potential through a conductor carrying a current:
where is the cross-sectional area of the conductor.