VMFL044
VMFL044
Supersonic
Nozzle Flow
Overview
| Reference | L.H. Back, P.F. Massier, H.L. Gier. "Convective Heat Transfer in a Convergent-Divergent Nozzle". Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, Vol. 7, pp. 549-568, 1964 | ||
| Solver | Ansys Fluent, Ansys CFX | ||
| Physics/Models | Compressible flow in supersonic regime, SST Model | ||
| Input File |
| ||
| Project Files | Link to Project Files Download Page |
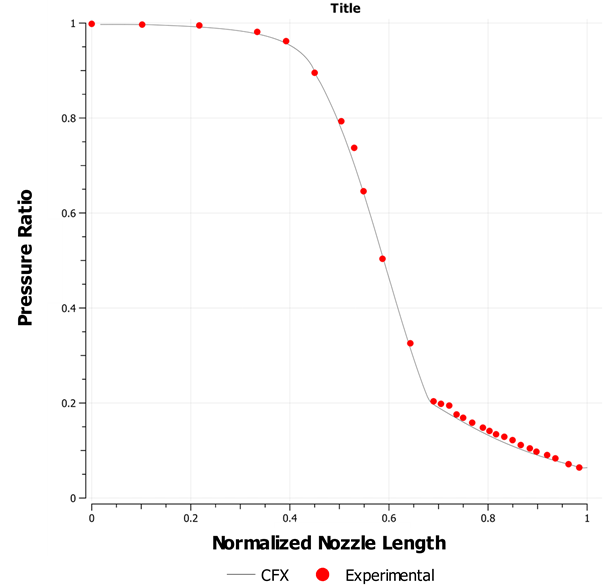
Test Case
Supersonic flow in a convergent-divergent nozzle is modeled. The flow is supersonic in the entire divergent section of the nozzle.
| Material Properties | Geometry | Boundary Conditions |
|---|---|---|
|
Density: Ideal Gas Viscosity: 1.831 X 10-5 kg/m-s |
Length of the nozzle = 0.1594 m Exit-to-throat area ratio = 2.68 Half angle of divergence = 15° |
Inlet Relative Pressure = 1 X 106 Pa Inlet Total Temperature = 825 K Wall temperature = 413 K |
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
The flow is steady. The walls are assumed to be at constant temperature. Only a 3° sector of the domain is modeled due to symmetry.