VMFL042
VMFL042
Turbulent
Mixing of Two Streams with Different Densities
Overview
| Reference |
| ||
| Solver | Ansys Fluent, Ansys CFX | ||
| Physics/Models | SST model, mixing layer, density difference, buoyancy | ||
| Input File |
| ||
| Project Files | Link to Project Files Download Page |
Test Case
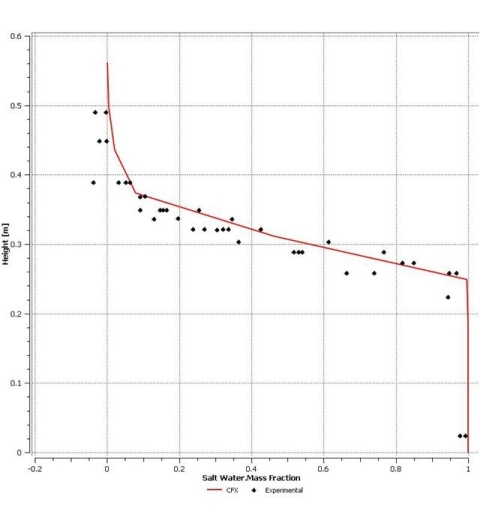
Mixing of two turbulent streams of fresh water and saline water is modeled. The two streams are parallel at the inlet and mixing proceeds downstream.
| Material Properties | Geometry | Boundary Conditions |
|---|---|---|
|
Density of fresh water: 1015 kg/m3 Density of saline water: 1030 kg/m3 Mixture kinematic diffusivity: 1 X 10-9 m2/s |
Length of the mixing duct = 40 m |
Fresh water inlet velocity = 0.52 m/s Salt water inlet velocity = 0.32 m/s |
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
The flow is steady. SST model is used. Buoyancy turbulence production option is used.