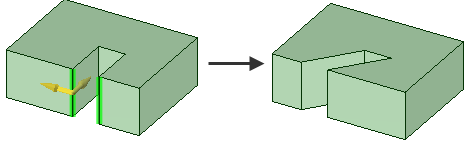
Pull Tool Examples
Pulling the edge of a surface first simplifies the edge, then its neighboring
edges are extended (or trimmed).
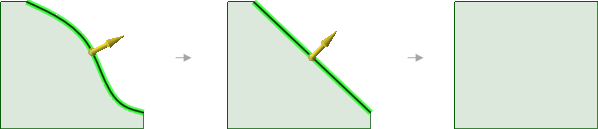
Pulling the edge of a surface while holding Ctrl makes
a new surface that is tangent to the edge..
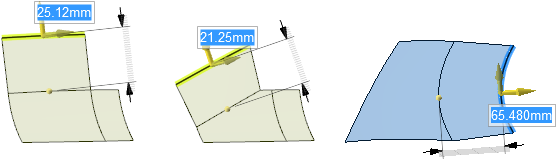
Pulling edges up to other edges with the Up To tool
guide.
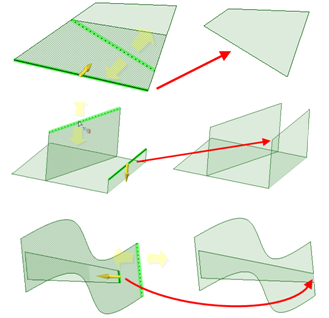
Pulling a point on a surface towards an Alt+clicked vertex.
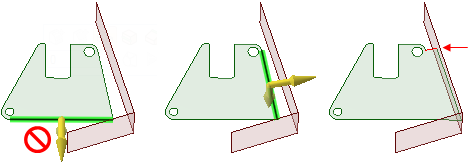
Pulling edges with the Full Pull option. If you select
the lower edge of the green surface shown below, you will receive an error
because the neighboring surface does not extend past the end of the selected
edge. The edge on the right side of the face can be pulled with the option,
because the neighboring face extends beyond its length. A new edge is created,
which is marked in red in the illustration on the right.
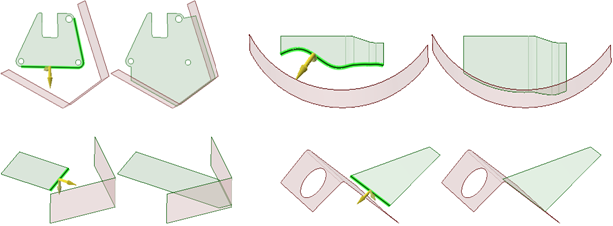
Pulling edges to their nearest neighbor with the Full
Pull option.
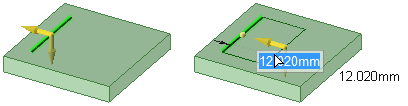
Pulling a sketched line on a planar face creates a surface in the same plane
as the face
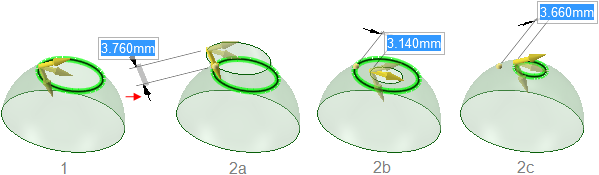
Pulling the edge of a toroidal surface. Three directions are available for
pulling.
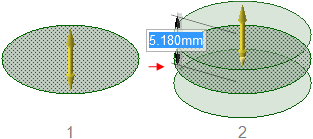
Holding Ctrl while pulling a surface with the
Both Sides option creates copies of a surface.
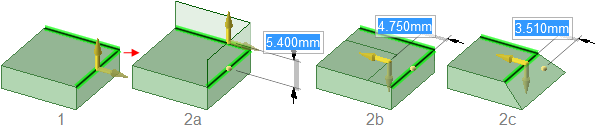
Pulling two edges with the Extrude (2a),
Copy Edge (2b), and Pivot (2c)
options.
Pulling a face offsets it, and its edges are influenced by neighboring
faces.
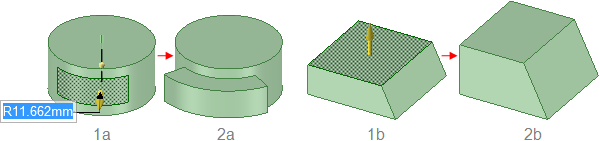
Pulling a face with its edges selected extrudes the face without influence
from neighboring faces.
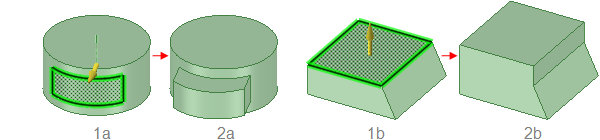
Pulling a conical face Up To a parallel cylindrical face replaces the cone
with the cylinder if the axes are close together. Otherwise, the conical face is
replaced with a cylindrical face that is coaxial to the cone and has the same
radius as the cylinder.
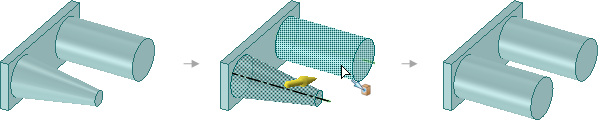
Pulling a pocket with rounded edges down through the bottom of a solid
transfers the rounds to the resulting hole.
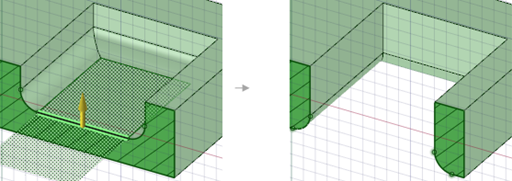
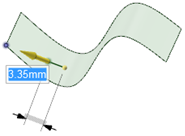
Pulling a surface up to a reference edge.
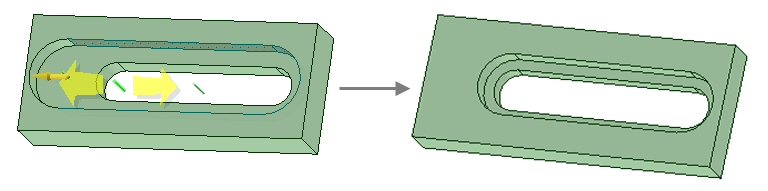
Pivot two separate edges together when pulling in one direction.