The Origin setting specifies 3D coordinates corresponding to the location of the new Coordinate Frame.
The X-Z Plane Pt setting specifies a point in the XZ plane used to define the positive X axis direction.
A coordinate frame is created by specifying three points. It is important to understand how these three points are used to create a coordinate frame.
The first point is the origin for the new coordinate frame (labelled Origin in the Definition tab). The second point is used to create a Z axis in the new frame. A vector is calculated from the Origin to the point defined in the Z Axis Point box and used as the third axis of the new coordinate frame. The plane normal to the Z axis is now set and contains both the X and Y axes.
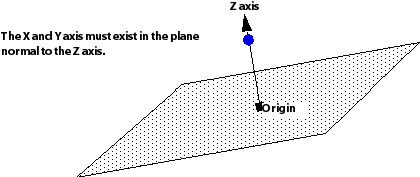
A third point entered into the X-Z Plane Pt box is needed to define the location of the X and Y axis in the plane normal to the Z axis. The X-Z Plane Pt point, along with the two points already specified, define a plane that lies in the X-Z plane (see diagram below). Because the X axis must now lie in both the X-Z plane and the plane normal to the Z axis, its location must be the line of intersection between the two planes. The positive direction for the X axis is the same side as the X-Z Plane Pt point lies with respect to the Z axis.
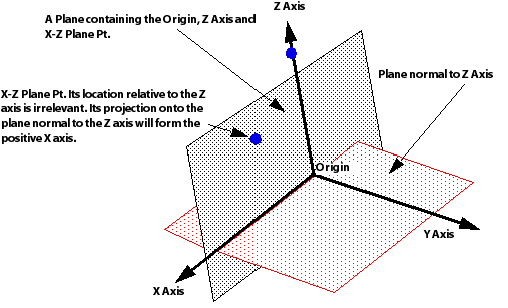
Finally, because the Y axis must be perpendicular to both the X Axis and the Z Axis, its positive direction is determined by the right-hand rule.
If X-Z Plane Pt is specified such that it lies on Axis 3, an error is displayed. The projection of the X-Z Plane Pt onto the plane normal to the Z axis would be on the origin and does not give enough information to define the X axis.


