VM14
VM14
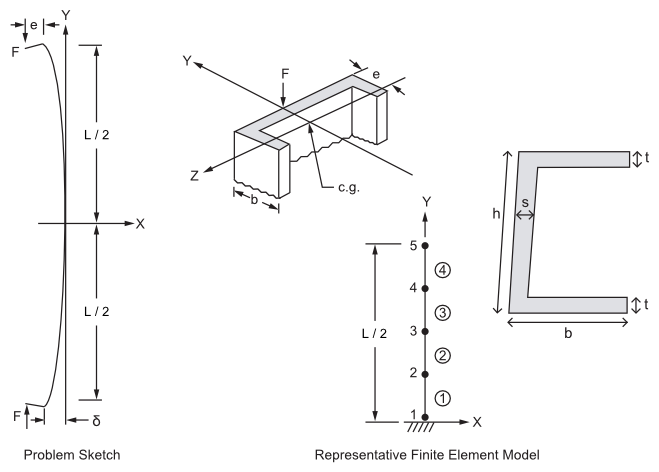
Large Deflection Eccentric Compression of a Column
Test Case
Find the deflection Δ at the middle and the maximum tensile
and compressive stresses in an eccentrically compressed steel strut
of length L. The cross-section
is a channel with the dimensions shown in the diagram. The ends are
pinned at the point of load application. The distance between the
centroid and the back of the channel is e, and the compressive force
F acts in the plane of the back of the channel and in the symmetry
plane of the channel.
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
Only one-half of the structure is modeled because of symmetry.
The boundary conditions for the equivalent half model become fixed-free.
Large deflection is needed since the stiffness of the structure and
the loading change significantly with deflection. The offset e is
defined in the element coordinate system.
Results Comparison
Solution recalculated
Corresponds to negative of X-deflection
at node 5