VM109
VM109
Temperature Response of a Suddenly Cooled Wire
Test Case
Determine the temperature response of a copper wire of diameter
d, originally at temperature To, when suddenly
immersed in air at temperature Tair. The convection
coefficient between the wire and the air is h.
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
The node locations are arbitrary (coincident). The final time
of 0.05 hr (180 sec) is sufficient for the theoretical response comparison.
An initial integration time step of 0.05/40 = 0.00125 hr is used.
Automatic time stepping is used. The thermal capacitance C, and
the surface area of the wire As, are calculated
based on a unit length as follows:
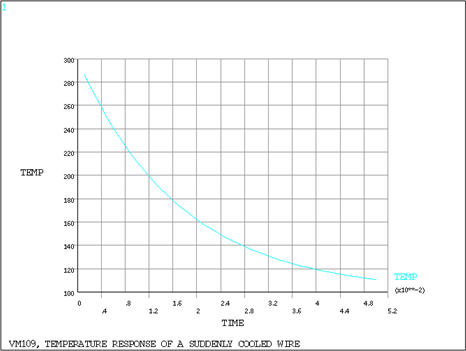
Results Comparison
POST26, Node 1 temperature history