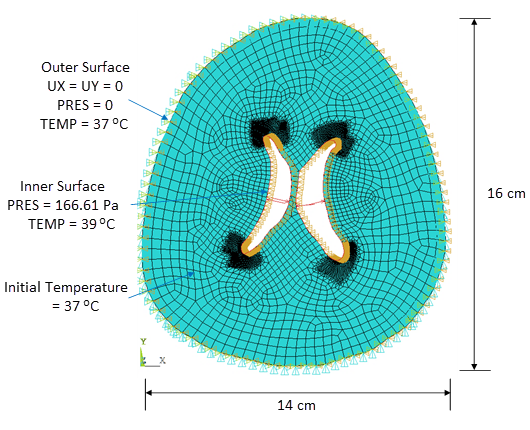
Hydrocephalus is a cerebral disease wherein the brain ventricles dilate and compress the parenchyma. The reference work [1] illustrates the ventricle dilation in an axial section of a brain captured by computed tomography (CT) scans in a patient with normal-pressure hydrocephalus. In our simulation, the following axial section of a brain tomography scan is considered for analysis:
Pressure and thermal loading will be applied to the ventricle. The soil analysis option (ANTYPE,SOIL) and consolidation option (SSOPT,CONSOLIDATION) are performed to determine the pore-pressure and temperature distributions.