FRF Estimation Overview
Sound: Analysis and Specification enables you to characterize the transfer function of a system by estimating its Frequency Response Function (FRF). For instance, you can estimate the FRF between the sound at a vehicle's HVAC vent and the sound that is received at the driver's position.
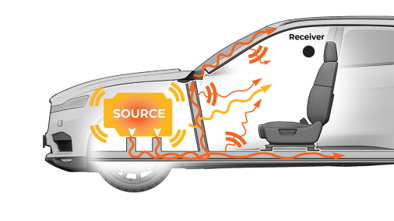
The FRF estimation module uses the H1 estimator, which is the method recommended to calculate the transfer function of a system between an input and an output, assuming that the noise is on the output.
The H1 estimator of the transfer function "H" between a source "X" and a receiver "Y" makes the assumption of a linear, time-invariant relationship between X and Y. The estimate of the transfer function H is then given in the frequency domain by H(f) = Pxy(f) / Pxx(f) where H is the transfer function, Pxy is the cross power spectral density between X and Y, and Pxx is the power spectral density of X. The Frequency Response Function estimate that is the output of the FRF estimation module is the magnitude of H(f) as a function of the frequency. The module's output is expressed in dB, and is similar to a gain.
After calculation, this module enables you to display and save the FRF. The FRF can be smoothed after estimation. Once you have saved the FRF file, you can then use the FRF in the filtering module to filter a measurement or signal. You can also use the FRF in the Sound Composer as a filter on a track. You can even use the FRF in Ansys Fluent to filter a simulation result.


