General
In Description box, you can type a comment line.
In Material Type box, you must select the material type.
Isotropic
The refractive index is constant in direction but it can vary with the wavelength.
Birefringent
This material has different refractive index associated with different crystallographic direction.
There is a reference in which this matrix is diagonal and whose diagonal elements correspond to the refractive index for different directions of the reference.
In Additional properties box, you must select Uniaxial negative, Uniaxial positive or Biaxial.
In Vector I and Vector J boxes, you must set coordinate values for Vector I and Vector J.
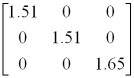
Fluorescent
The material includes fluorescent dyes.
The fluorescent material usage is the same as any other material. The only difference is that you can enter fluorescence specific data as absorption spectrum, re-emission spectrum, quantum efficiency, measure concentration and user concentration.
In Fluorescent tab, you can Add
 or Delete
or Delete
 pigment. You can click to edit measured or user
concentration. Measured concentration is the dye concentration
when the fluorescent dye has been measured. User concentration is
the concentration defined by the user for simulations.
pigment. You can click to edit measured or user
concentration. Measured concentration is the dye concentration
when the fluorescent dye has been measured. User concentration is
the concentration defined by the user for simulations.
Metallic
The metallic material correctly interacts with polarized light. Since the polarization is taken into account, the material's reflectance changes when the incidence angle varies.
When you apply this material to a part, the reflection automatically takes the effects due to polarization into account.
The Absorption variation and Scattering properties tabs are displayed but are of no use for the Metallic material type. You do not need to set them as their definitions have no effect on the Metallic material type.


