Absorption Variation
The concentration parameters are used when the absorption is due to a pigment diluted in a main material, typically a colored plastic.
Absorption Calculation
The term absorption refers to the physical process of absorbing light, while absorbance does not always measure absorption: it measures attenuation of transmitted radiant power. Attenuation can be caused by absorption, but also reflection, scattering, and other physical processes.
Absorption (or attenuation) coefficient= 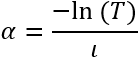
- Propagation distance l is the distance traveled)
Transmittance is given by:
T(l) = exp(-α*l) or when taking into account Fresnel reflection or entrance diopter: T(l) = T(0)*exp (-α*l).
Measured Concentration
When you measure the optical absorption of a plastic that has a known pigment concentration also called Measured concentration, you put this absorption in the material absorption table.
User Concentration
The User concentration is the pigment concentration used for the simulation.
If the user concentration is the same as the measured concentration, then you are simulating using exactly the plastic you measured.
You have the possibility to do a simulation with a plastic that has a different pigment concentration without having to create and measure a new piece of plastic. You have to put the new concentration in the User concentration box. You are now ready to simulate. The software computes the new absorption from the absorption spectrum, the measure concentration and the user concentration.
 or Delete
or Delete
 a column.
a column.

