Biconic Lens
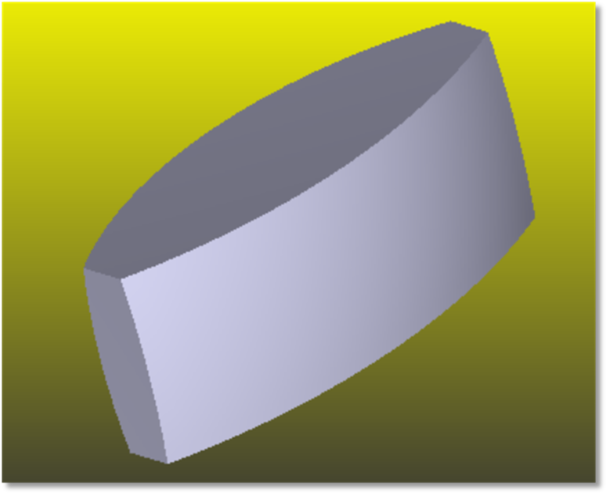
A biconic lens is similar to a toroidal lens, except the conic constant and base radius may be different in the X and Y directions. The biconic lens allows specification of Rx, Ry, Kx, and Ky for the front and back surfaces independently. The sag of a biconic surface is given by:
Where
and
The biconic lens is defined by these parameters:
| Parameter # | Description | Face Name | Face # |
| 1 | The radial height of the lens object in lens units. This value is used for the y direction half height if the lens is rectangular. | NA | NA |
| 2 | The x half width of the lens object in lens units. If zero, the lens is circular; otherwise, the lens is rectangular. | NA | NA |
| 3 | The center thickness of the lens in lens units. | Side | 0 |
| 4-5 | Unused. | NA | NA |
| 6 | The base radius of curvature in the XZ plane for the front surface. If this value is zero, then the XZ curvature is assumed to be zero. | Front | 1 |
| 7 | The base radius of curvature in the YZ plane for the front surface. If this value is zero, then the YZ curvature is assumed to be zero. | Front | 1 |
| 8 | The X direction conic for the front surface. | Front | 1 |
| 9 | The Y direction conic for the front surface. | Front | 1 |
| 10 | The base radius of curvature in the XZ plane for the back surface. If this value is zero, then the XZ curvature is assumed to be zero. | Back | 2 |
| 11 | The base radius of curvature in the YZ plane for the back surface. If this value is zero, then the YZ curvature is assumed to be zero. | Back | 2 |
| 12 | The X direction conic for the back surface. | Back | 2 |
| 13 | The Y direction conic for the back surface. | Back | 2 |
Face Numbers: Front face Face 1, back face Face 2, all other faces Face 0.
Next:


