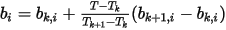Temperature-Dependent B-H Curves
While a material’s temperature dependency can be specified via the thermal modifier, which is described in terms of a mathematical expression, this might not be good enough for applications where it is difficult to describe the temperature dependency in terms of an expression. For such cases, an alternative method is available to let users directly input data for multiple, temperature-dependent, B-H curves. Maxwell uses this data to derive a corresponding B-H curve for each specified temperature using an interpolation algorithm as follows:
Suppose there are m temperature dependent curve inputs in the form of:
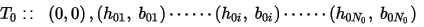
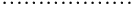
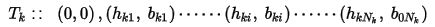
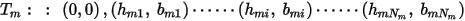
Where T0, Tk, and Tm …(T0 < Tk < Tm) are reference temperatures at which B-H curves were measured.
The number of (b,h) pairs in each BH curve can be different.
In Maxwell, if the local temperature of temperature-dependent nonlinear magnetic material is T.. 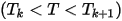 , the local B-H curve can be obtained by interpolation:
, the local B-H curve can be obtained by interpolation:
If T ≤ T0, B-H curve input at temperature T0 is applied.
If T ≥ Tm, B-H curve input at temperature Tm is applied.
If Tk < T < Tk+1, (hi, bi) pairs are calculated as:
For a given hi, bk,i, and bk+1, i is the magnetic flux densities obtained from inputted B-H curves at temperatures Tk , Tk+1, and bi is obtained by interpolation: