Material Coordinate Systems
Maxwell supports the following three types of coordinate systems, which can be used to define some vector or anisotropic material properties:
- Cartesian (defined by the X, Y, and Z axes)
- Cylindrical (defined by the R, Phi, and Z axes)
- Spherical (defined by the Rho, Theta, and Phi
axes)
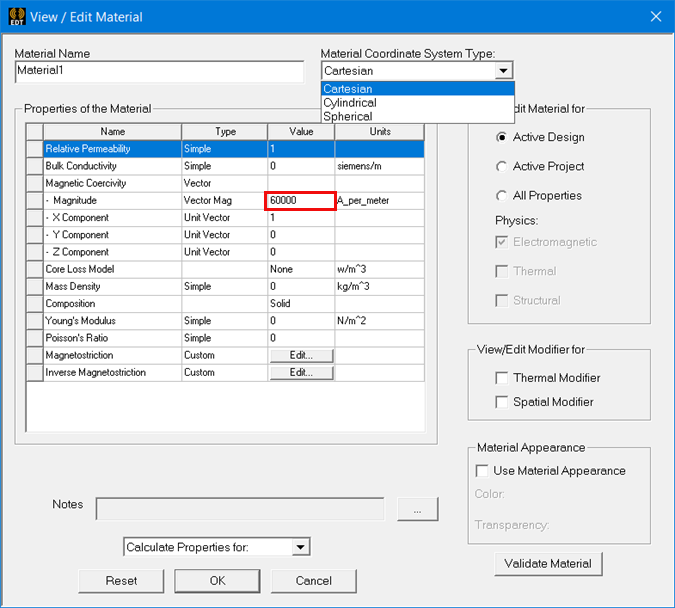
To get the fields for the vector magnetic coercivity vector, a non-zero value must first be specified for the magnitude of the vector. The magnitude can also be functional. The magnitude of the magnetic coercivity is expected to be < 0. If you use a positive value, the direction used will be the opposite of the unit vector specified.
