Eddy Current Theory
Time-varying currents flowing in a conductor produce a time-varying magnetic field in planes perpendicular to the conductor. In turn, this magnetic field induces eddy currents in the source conductor and in any other conductor parallel to it. The eddy current field solver calculates the eddy currents by solving for A and F in the field equation:
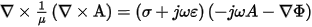
where:
- A is the magnetic vector potential.
- F is the electric scalar potential.
- m is the absolute magnetic permeability.
- w is the angular frequency at which all quantities are oscillating.
- s is the conductivity.
- e is the absolute permittivity.
Note:
The eddy current
equation is derived from Maxwell’s equations. Phasor
notation is used to represent complex quantities.
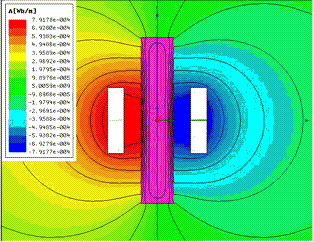
A plot of flux lines produced by eddy currents that were computed in a structure by the eddy current solver is shown below: