3D Clone Mesh Generation
The 3D clone mesh is generated only when the following conditions are met:
-
The TAU mesher is selected in the Maxwell 3D > Mesh > Initial Mesh Settings window.
-
The Cylindrical Gap mesh operation has been assigned in the Cylindrical Gap Mesh Operation window.
-
The Clone Mesh check box is checked.
-
The model has a stator with more than two teeth.
The solid bodies adjacent to the band are detected to identify the clone object. If the object has more than two teeth that are close to the band, the teeth will be verified to see they have the identical geometric features. If the teeth are skewed, TAU will fall back to the regular mesh. Otherwise the region from the radius of teeth to the outer edge of the object will be further classified and verified to see if the object has the multiple 3D identical sub-regions.
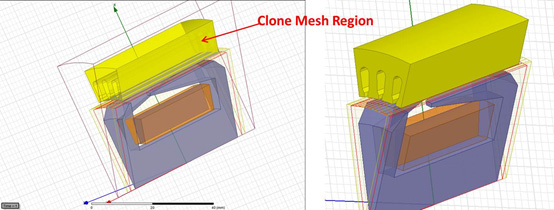
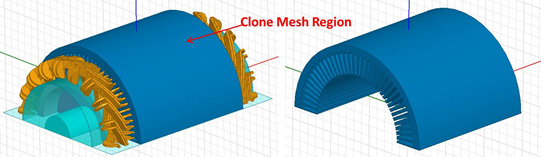
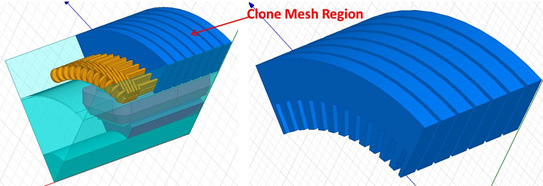
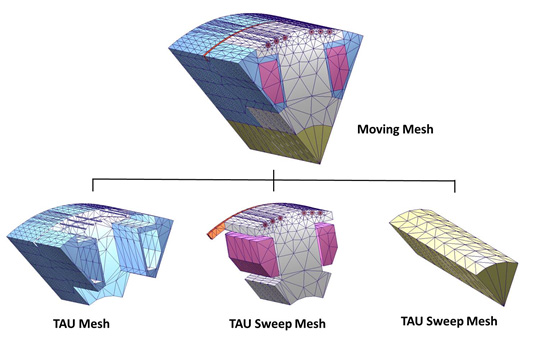
If a 3D clone region has been identified, TAU will classify the 3D rotational model into a static region and a moving region by the band object radius. The Static region includes the clone region and skewed coils regions at one side or two sides. Clone mesh method will then be used to generate the mesh in the clone region, while the TAU regular mesh method will be used to generate the mesh at other skewed regions.
The moving region includes skewed coils regions in which the TAU regular mesh method is used to generate the mesh, and also the non-skewed sweep regions in which the TAU sweep mesh method is used to make the mesh.
3D Clone Mesh
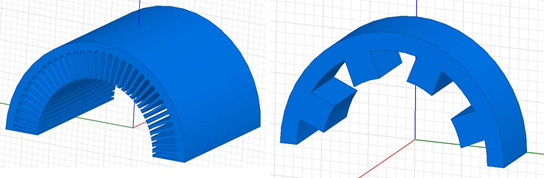
A 3D clone region may have only one simple object, or several sections of clone objects with the gap between as shown in the following images.
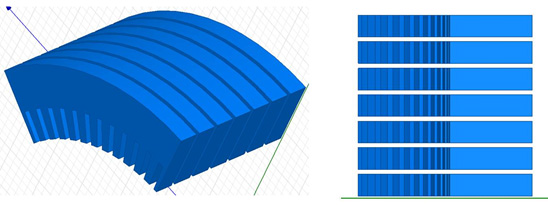
To ensure the identical volume mesh in each sub-region, the volume mesh is generated in the Master region, then by using a copy-and-paste method to duplicate the mesh at all child regions. In the 3D master region, if the region is also symmetric, then a symmetric mesh is generated. Sweeping mesh technology is used to make the volume mesh in the master region. In the half of the master region, a surface mesh is generated at the axis side. The volume mesh is generated by sweeping the surface mesh in the axis direction to fulfill the clone master region.
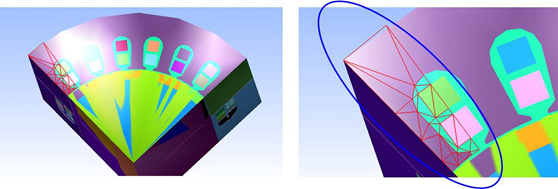
The volume mesh will be mirrored to the other half of the master region to produce the symmetric mesh in the master region.
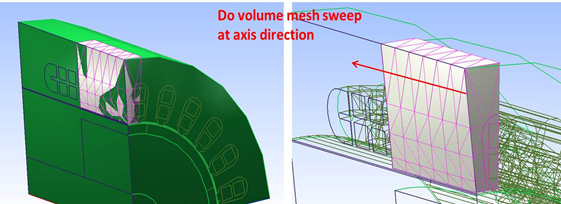
The volume mesh in the master region is then duplicated and translated to the child regions with copy and paste technology in TAU to complete the 3D clone region mesh.
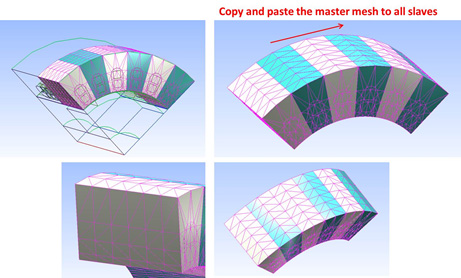
3D TAU Mesh
Beyond the 3D clone region, normally the regions have skewed coils. Therefore TAU regular mesher will be used to make the mesh.
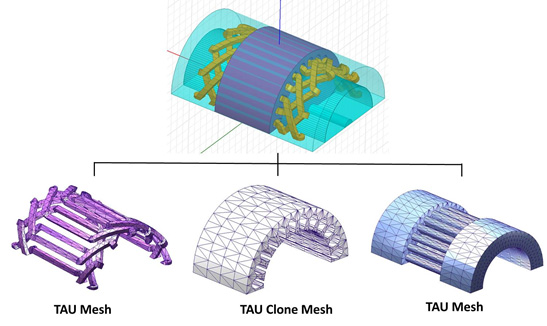
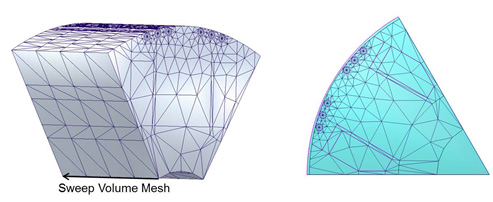
3D Sweep Mesh
The rotational model for a moving region may have different structures. It may have all skewed coils and rotors. In this case, the TAU regular mesh will be used to make the mesh.
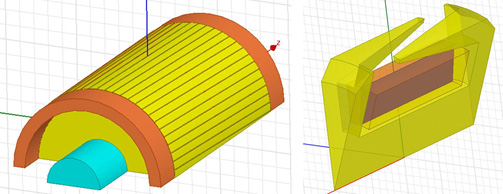
At the axis direction, the moving region can be classified into several specific regions. If the region has skewed objects, it is called a “regular section,” and the TAU regular mesh is applied. If the region can be geometrically sweeping at the axis direction, the region is called a sweep region, and the TAU sweep mesh method is applied.
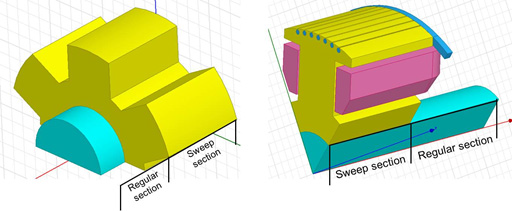
For the sweep section, a surface mesh is generated at the side, then the volume mesh is made by sweeping the surface mesh in the axis direction. This ensures a uniform mesh in the rotational direction, while maintaining the long aspect ratio in the axis direction to keep the mesh size small.
The volume mesh for the rest of the regions is made by the TAU regular mesher.