Finite Conductivity Boundaries
In HFSS, finite conductivity boundaries represent imperfect conductors.
At such boundaries, the following equation holds:
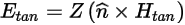
where:
- Etan is the component of the E-field that is tangential to the surface.
- Htan is the component of the H-field that is tangential to the surface.
- Zs is the surface impedance of the boundary. When the thickness is much larger than the skin depth,
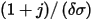 can be used. When not, Zs can be calculated from the transmission line model used at a layer impedance boundary condition.
can be used. When not, Zs can be calculated from the transmission line model used at a layer impedance boundary condition. - δ is the skin depth
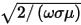 of the conductor being modeled.
of the conductor being modeled. - ω is the frequency of the excitation wave in radians/second.
- σ is the conductivity of the conductor.
- μ is the permeability of the conductor.
The fact that the E-field has a tangential component at the surface of imperfect conductors simulates the case in which the surface is lossy.
The surfaces of any objects defined to be non-perfect conductors are automatically set to finite conductivity boundaries.
HFSS does not attempt to compute the field inside these objects; the finite conductivity boundary approximates the behavior of the field at the surfaces of the objects.
The finite conductivity boundary condition is valid only if the conductor being modeled is a good conductor; that is, if the conductor's thickness is much larger than the skin depth in the given frequency range. If the conductor's thickness is in the range or larger than the skin depth in the given frequency range and has been defined, HFSS takes the thickness into account.
