Adding 3D Datasets
HFSS, Maxwell, and Icepak designs support 3D datasets (representing a spatial or volumetric profile). Depending on which of these three design types you are using, you will be able to create only design-level 3D datasets, only project-level 3D datasets, or both.
In HFSS designs, you can define only project-level 3D datasets (used for the definition of material properties that vary according to the spatial coordinates).
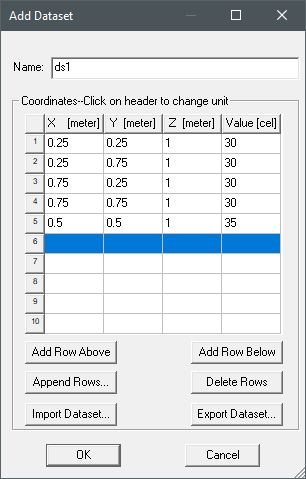
To define a 3D dataset, specify a list of X, Y, and Z coordinates and the corresponding Values in the Add Dataset window. For example, the first line in the image below specifies a temperature of 30° C at (0.25, 0.25, 1). The data specifies a variation of temperature on the plane 0.25 ≤ X ≤ 0.75, 0.25 ≤ Y ≤ 0.75, Z = 1. In this example, the values in the Values column are temperature, but can be set to a different unit depending on the property you wish to assign. To change the unit, click the X, Y, Z, or Value header row.
- Using the menu bar, click Project
> Datasets or, on the Desktop ribbon tab, click
 Datasets.
Datasets.
The Datasets dialog box appears. This lists any existing datasets.
- Click Add > Add 3D Dataset.
The Add Dataset window appears.
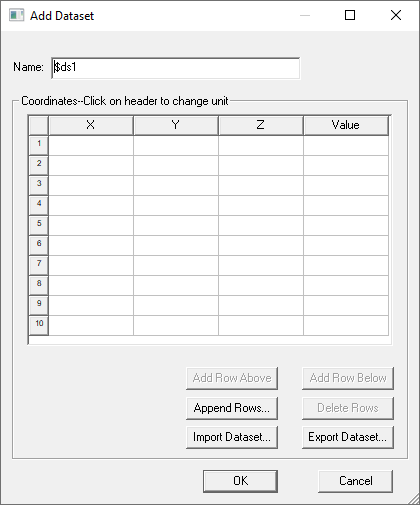
The window contains fields for the dataset name and a table for X, Y, and Z coordinates and corresponding values. It can be resized to display additional rows and columns, and includes buttons for the following functions:
- Add Row Above – adds a new row to the table above the selected row.
- Add Row Below – adds a new row to the table below the selected row.
- Append Row – opens a dialog box that lets you specify a number of rows to add to the table.
- Delete Row – deletes the selected row or rows.
- Import Dataset – this provides a way to import data sets from an external source. The format is a tab separated points file. Clicking the button opens a file browser window.
- Export Dataset – this provides a way to export the current dataset to a tab separated points file. Clicking the button opens a file browser window.
- Optionally, type a name other than the default for the dataset in the Name field.
- Click the X, Y, Z and Value column headers to select a
unit category. The default is No Unit.
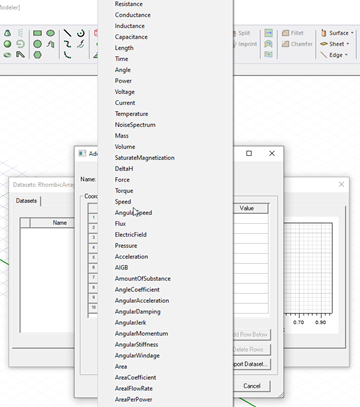
Click the header again to select a unit in that category. You can select No unit.
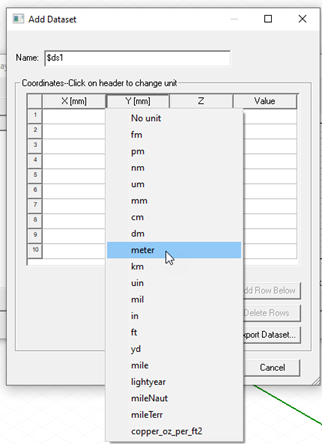
Selected units are displayed for each column in the header cell.
- Enter the X, Y, and Z coordinates and the corresponding values by one of the following methods:
- Import Dataset
- Type coordinates and associated value in the X, Y, Z, and Value columns.
- When you are finished entering the data point coordinates and values, click OK.
When used with a clp function (Closest point interpolation) in an expression, performance will degrade with large 3D dataset.
