Specifying Thermal Modifiers
Thermal modifiers are multiplicative in nature and assigning them introduces spatial dependence. Because you cannot have spatial dependence and causality, Ansys Electronics Desktop ignores Auto Causal Materials options when a thermal modifier exists.
To specify thermal modifiers for a material:
- In the View/Edit Material dialog box, you must enable the Thermal Modifier check box:
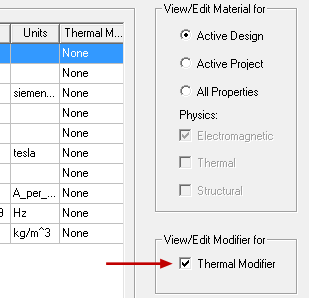
This option causes the properties table to expand to include a Thermal Modifier column.
By default, the Thermal Modifier option is set to None for all material properties.
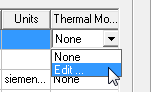
- Click a Thermal Modifier cell and select Edit... from the drop-down menu:
The Edit Thermal Modifier dialog box appears with the Expression option selected.
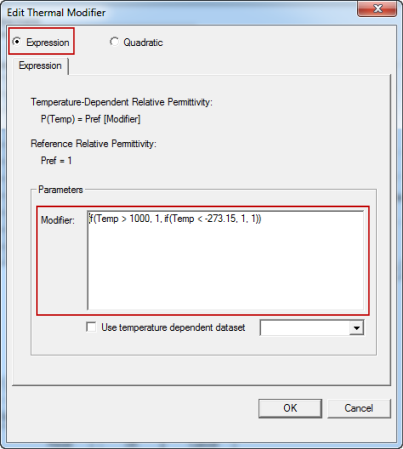
With this option selected, the Modifier text box is displayed under Parameters. This text box contains a conditional expression template, which you can use as a starting point for creating your own expression. The property for which the multiplier is being defined and its nominal value are indicated above the Parameters section.
- With Expression selected, you can write an equation for a thermal modifier in the Modifier text box.
The following example defines a multiplier that varies linearly from 1.1 (at 0° C) to 0.2 (at 1000° C). The multiplier is constant at 1.1 for temperatures below 0° C and constant at 0.2 for temperature above 1000° C:
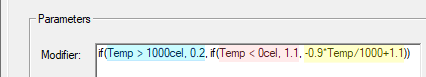
In this example, the linear equation -0.9 * Temp / 1000 + 1.1 (highlighted in yellow) defines the multiplier for the range 0° C ≤ Temp ≤ 1000° C.
The default unit of temperature in thermal modifier expressions is Celsius (cel). However, you can override the units by appending the appropriate abbreviation to the numbers in the expression (mkel, ckel, dkel, kel, cel, rank, fah). Model temperatures, material properties, and thermal modifiers need not have consistent units; values are converted automatically as needed.
- Check Use temperature dependent data set to disable the Modifier text box. You can then use the drop-down menu at the bottom-right corner of the dialog box to select an existing project dataset or to create a new one by choosing Add/Import Dataset.
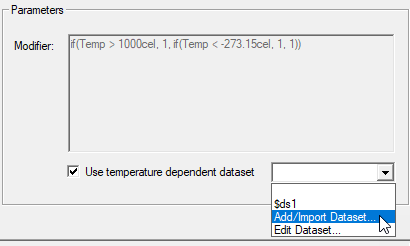
This command lets you define the thermal modifier dataset (a set of X and Y values). Alternatively, if a suitable project dataset already exists, it will be available for selection from the same drop-down menu.
When creating a new dataset, the X values are temperatures, and the Y values are the corresponding thermal modifiers. The value of the nominal material property is multiplied by this thermal modifier to determine the resultant property at a given temperature. The modifier is interpolated linearly between specified data points.
The following example is a dataset defining thermal multipliers for the thermal expansion coefficient (TEC) of an aluminum-beryllium alloy. The temperature range is -150 to 250° C, and the nominal value (corresponding to 20° C) is 1.37e‑5/°C:
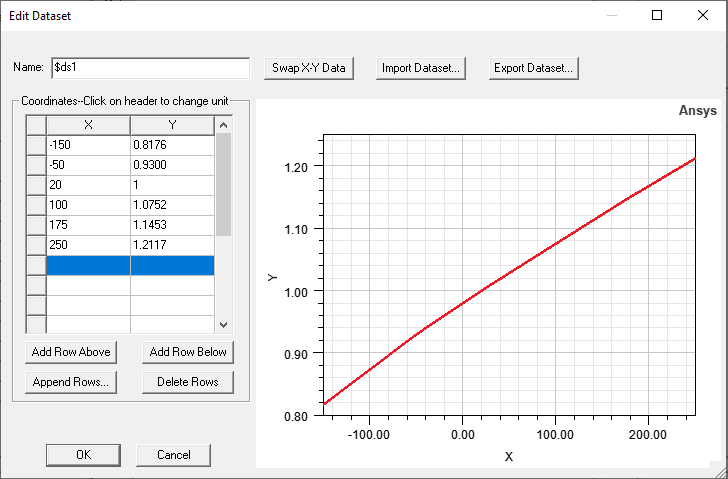
Based on these multipliers, the resultant TEC at -150° C is approximately 1.12e‑5 (= 1.37e‑5 * 0.8176), and the TEC at 250° C is 1.66e‑5 (= 1.37e‑5 * 1.2117).
In addition to filling the table of values manually, you can also Import an existing tab-delimited file to create the dataset.
Important:When you add a dataset from the Edit Thermal Modifier dialog box, you cannot specify the temperature units. The numbers in the X column will be interpreted as degrees Celcius and cannot be changed. Also, you cannot append a unit abbreviation (such as "fah" or "cel") to the numbers. You must enter temperature values in degrees Celcius for correct results. The values in the Y column are multipliers and therefore dimensionless.
Alternatively, you can create a dataset based on any desired temperature units before defining your temperature-dependent material properties. To do so, click Project> Datasets from the menu bar and then choose Add. If your project includes a design type that supports 3D datasets, a submenu appears offering a choice of a 1D or 3D dataset. If you see this choice, click 1D. In either case, the Add Dataset dialog box appears.
For the dataset to be used later as a thermal modifier, you must click the X column header and choose Temperature. Then, click the X column header again and choose the desired temperature units. Finally, populate the table with your temperature and multiplier values and then click OK and Done. The dataset will now be available for selection from the drop-down menu in the Edit Thermal Modifier dialog box.
After choosing or creating a dataset, it appears in the Modifier field of the Edit Thermal Modifier dialog box, as shown in the following image:
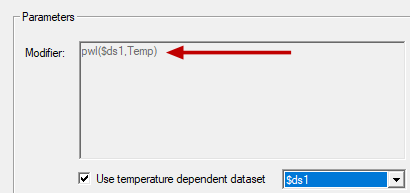
The syntax of the dataset expression is explained as follows:
- pwl: Type of dataset – Piecewise linear
- $ds1: Name of an existing dataset – "$" indicates a project dataset, which is a requirement for thermal modifiers
- Temp: Type of X value – Temperatures
The Y values in this case are simple multipliers and therefore unitless.
Note:To edit an existing dataset, select Edit Dataset from the drop-down menu in the Edit Thermal Modifier dialog box. The Datasets dialog box appears. Select the dataset to modify and click Edit.
- With Expression selected, you can write an equation for a thermal modifier in the Modifier text box.
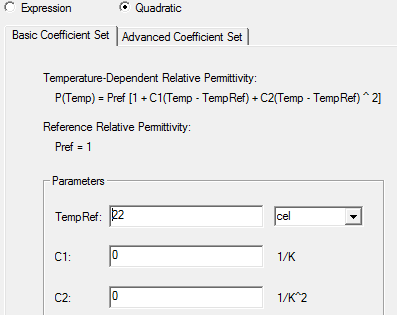
- Alternatively, select the Quadratic option to display the tabs for Basic Coefficient Set and Advanced Coefficient Set (as shown below):
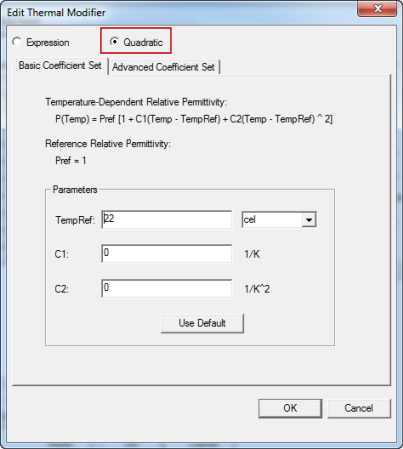
- Under the Basic Coefficient Set tab, you can edit fields for the TempRef and units, and fields for C1 and C2 for the following equation:
P(Temp) = Pref[1+ C1(Temp - TempRef) + C2(Temp - TempRef)^2]
where TempRef is 22 cel by default and where the Pref is defined as the reference relative permittivity.
 Note:
Note:The coefficients, C1 and C2, should be negative to yield physical results.
- Under the Advanced Coefficient Set tab, you can edit fields for lower and upper temperature limits (TL and TU, respectively) and select their units from the drop-down menu.
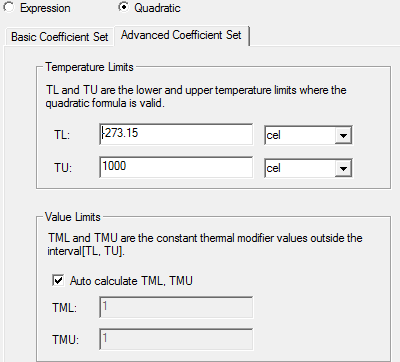
You can also edit the constant value limit for the thermal modifier values outside the limits. By default, these are automatically calculated. Uncheck the Auto Calculate TML and TMU to specify new values for thermal modifier lower (TML) and thermal modifier upper (TMU).
- Under the Basic Coefficient Set tab, you can edit fields for the TempRef and units, and fields for C1 and C2 for the following equation:
- Click OK to accept your edits and return to the View/Edit materials dialog box.
