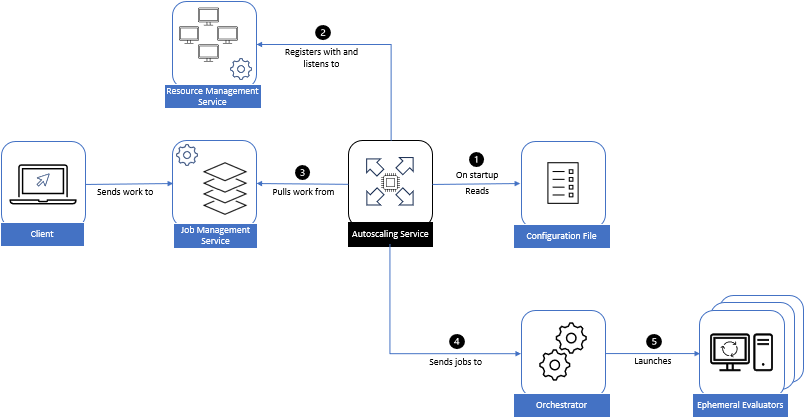
An Autoscaler (sometimes referred to as a Scaler) is a specialized worker agent used in dynamic or autoscaling deployments. Instead of directly running simulation tasks itself, its main role is to automatically launch Evaluators based on the current workload demand.
Key functions of an Autoscaler:
Monitors demand: It interacts with the Ansys HPC Platform Services system to understand the queue of pending tasks.
Interfaces with schedulers/orchestrators: Based on demand, it submits jobs to traditional HPC job schedulers (like SLURM, LSF, PBS, UGE) or requests resources from cloud-native orchestrators (like Kubernetes).
Launches ephemeral evaluators: The jobs or pods started by the Autoscaler will typically contain and run an ephemeral (temporary) Evaluator instance. This newly launched Evaluator then connects to the core services and picks up tasks for which it is suited.
Registration: Like other workers, the Autoscaler itself also registers with the Resource Management Service (RMS).
How It Works
In an autoscaling deployment of evaluators, jobs run on an orchestrator. An Autoscaling Service launches the required number of evaluators (workers) to meet the demand of the workload. It does this by submitting jobs to traditional job schedulers (Slurm, LSF, PBS, or UGE), or the cloud-native orchestrator Kubernetes.
As the jobs start on the orchestrator, or extra pods are launched in the case of Kubernetes deployments, ephemeral evaluators are spawned and pick up tasks that can be executed by their associated resources. Evaluators spawned this way tend to be more tied to the requested workload.
On startup, an autoscaler registers itself with the Resource Management Service and periodically re-registers and looks for configuration updates that it then applies to its configuration file.