Sharp Angle Face Removal control allows you to remove the sharp angle faces below the specified angle tolerance by merging them to the neighboring faces.
Sharp Angle Face Removal Details view has the following options:
General
Control Type: Displays the selected control type.
Scope
Define By: Allows you to define the input to the selected control. The available options are Value and Outcome.
Value: Allows you to manually set the value of the Scoping Method and Scoping Pattern.
Outcome: Allows you to select the existing scoped outcomes from the previous steps as input.
Scoping Method: Allows you to select the entities for the selected control. The available options are:
Part: Allows you to select parts for defining the scope of the control.
Label: Allows you to select labels for defining the scope of the control.
Zone: Allows you to select zones for defining the scope of the control.
Scoping Pattern: Allows you to specify the name pattern to get the selected Scoping Method. Scoping Pattern supports Regular Expression. You can click
 on the right corner of the option and the
following options are available:
on the right corner of the option and the
following options are available:Publish: Publishes Scoping Pattern to the Property Worksheet.
Scope All: Inserts '.*' regular expression to scope all entities.
Definition
Sharp Angle : Allows you to capture faces below the specified angle. The default value for Sharp Angle is 10 degrees. You can click
 on the right corner of the option and click
Publish to publish Sharp Angle to
the Property Worksheet. You can parametrize
Sharp Angle.
on the right corner of the option and click
Publish to publish Sharp Angle to
the Property Worksheet. You can parametrize
Sharp Angle.Feature Angle: Specifies the minimum dihedral angle at which the geometry features are repaired. The default value is 30 degrees. You can provide any value between 0 to 180 degrees.
You can click
 on the right
corner of the option and click Publish to publish
Feature Angle to the Property
Worksheet. You can parametrize Feature
Angle. Feature Angle is the dihedral angle
measured as follows:
on the right
corner of the option and click Publish to publish
Feature Angle to the Property
Worksheet. You can parametrize Feature
Angle. Feature Angle is the dihedral angle
measured as follows: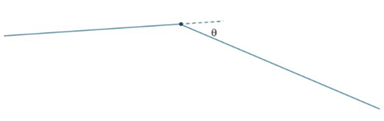
When θ = 0, two surfaces are perfectly tangential, and the edges are not protected. Hence, the two surfaces can be merged, or edges can be suppressed, pinched or more.
When 30 ≤ θ ≤ 90 degrees, the edges between the two surfaces are protected and cannot perform merging or pinching at the location.
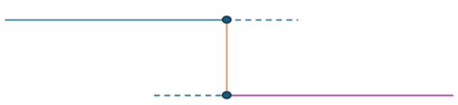
θ = 90
When θ > 90 degrees, the surfaces are not protected and prevent topology operations like merge or pinch on faces or edges.


