To use Server of Servers, depending on the method of spatial partitioning (Externally partitioned, Reader partitioned, or Server partitioned) described above, you do the following:
External Partitioning
Partition your data, and distribute it (or make it available) to the various machines on which you will run servers.
Create the sos casefile, which defines the data format to use, the server machines, the location of server executables on those machines, and the name and location of the [partitioned] data for the servers.
Important: Each server in the casefile will reference different data. Examples will be shown below.
Run EnSight with the
-soscommand line option(or useensight.sosin place ofensight_serverif connecting manually) and provide it with the sos casefile. You can run EnSight like:ensight -sos.
Then under → , set the sos casefile under the Data tab, with a format of Case SOS.
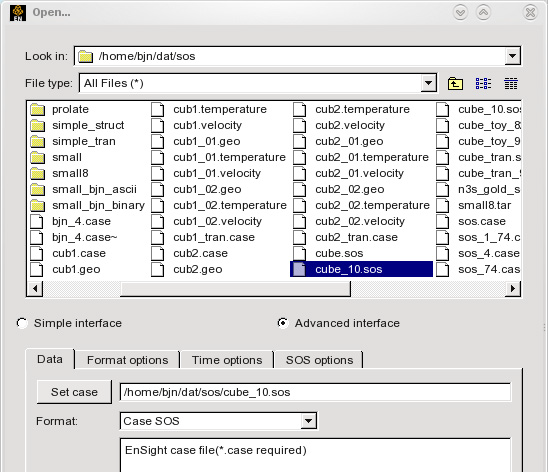
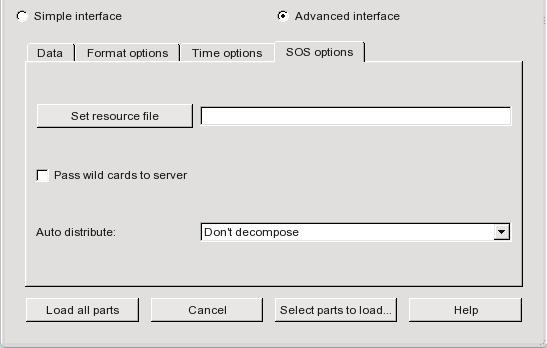
Under the SOS options tab, you can verify that Auto distribute is set to Don’t decompose (because the data is already decomposed).
Using the command in this way runs the SOS on the same machine as the client. If you want to control where the SOS runs, connect manually instead (a manual example will be shown later in this article). Also note that if you want to load all parts, you could have simply included the sos casefile on the command line, like:
ensight -sos /home/bjn/dat/sos/cube_10.sos
Additionally, you can use resources in combination with a sos casefile if desired. See Use Resource Management for an example.
Spatial Partitioning Done by a Reader, "Auto Distribute Reader Decompose"
If your reader can do its own partitioning, you can use an sos casefile in which each server references the same data, OR take advantage of a resource file and not have to create an sos casefile. Note that for this method, under the SOS options tab in the File → Open dialog, you will see that Auto distribute is set to Reader Decompose.

It is probably easiest to describe the usage based on an example. So using the Exodus reader, lets run an Exodus model on two servers (computer1 and computer2), first using the .sos case file and then the .res file (you don't use them both at the same time). The files we will reference are:
sample.exo (the Exodus data file)
servers.sos (the SOS casefile)
FORMAT type: master_server MultiExodusII SERVERS number of servers: 2 #Server 1 #------------ machine id: computer1 executable: ensight_server data_path: /home/user/exodus casefile: sample.exo #Server 2 #------------ machine id: computer2 executable: ensight_server data_path: /home/user/exodus casefile: sample.exo
servers.res (the resource file, see Use Resource Management for more details)
#!CEIResourceFile 1.0 SOS: host: localhost SERVER: host: computer1 host: computer2
Flow3D SOS Case file example which uses two computers (computer1 and computer2), and 4 servers, with 4 files (flsgrf1.dat, flsgrf2.dat, flsgrf3.dat and flsgrf4.dat) located on a common file system that both computers can read: /scratch/data/lowres and perhaps name it servers.sos. It will also be necessary that the machine where you start up your server of server has the Flow3d reader (must be either a Linux or windows machine) and it is able to start up servers using passwordless ssh.
FORMAT type: master_server Flow3D-Multiblock SERVERS number of servers: 4 #Server 1 #------------ machine id: computer1 # for same machine use #machine id: localhost executable: ensight_server # for windows use #executable: ensight_server data_path: /scratch/data/lowres/ casefile: flsgrf*.dat #Server 2 #------------ machine id: computer1 executable: ensight_server data_path: /scratch/data/lowres/ casefile: flsgrf*.dat #Server 3 #------------ machine id: computer2 executable: ensight_server data_path: /scratch/data/lowres/ casefile: flsgrf*.dat #Server 4 #------------ machine id: computer2 executable: ensight_server data_path: /scratch/data/lowres/ casefile: flsgrf*.dat
Your servers.res file will be the same as above except it will have four servers, and perhaps named four_servers.res.
#!CEIResourceFile 1.0 SOS: host: localhost SERVER: host: computer1 host: computer1 host: computer2 host: computer2
For the exodus example above, make sure your sample.exo data file is available to the various computers on which you will run servers. For the Flow3d example above, make sure all four flsgrf*.dat files are in the same directory and available to all the computers.
Create the sos casefile, Or the resource file appropriate for your format above (use one or the other). You can copy/paste from the examples above.
Run EnSight using one of the following (not both):
ensight -sosThen set the
servers.sosfile in the File → Open dialog (format Case SOS). This enables you to load all parts, or select the ones to be loaded. Or useensight -sos servers.soson the command line if you want to load all parts.-- OR if you want to use the resource (.res) file --
Choose the sample.exo file or the flsgrf*.dat in the File → Open dialog (format MultExodusII, format Flow3d-Multiblock respectively), and place the appropriate .res file in the Set resource file field under the SOS options tab. For Flow3d data, toggle ON the Pass wild cards to server option, which will allow the asterisk in flsgrf*.dat to pass down to the servers to handle appropriately. This enables you to load all parts, or select the ones to be loaded. Or use
ensight -sos -res servers.reson the command line and set sample.exo (or flsgrf*.dat) file in the File → Open dialog (format MultExodusII, Flow3D-Multiblock, respectively). Or, for exodus format, useensight -sos -res servers.ressample.exo on the command line if you want to load all parts. You cannot use the command line for Flow3D format because you must tell EnSight to pass the asterisk to the servers and this appears to only work from the dialog.There are several other variations that could be used, including the use of a manual connection with the SOS. They all have similar corresponding options.
Spatial Partitioning by EnSight Servers "Auto_distribute (Server Decompose)
You can let EnSight do the partitioning. You can use an sos casefile in which each server references the same data, or take advantage of a resource file and not have to create an sos casefile.
Note: For this method, under the SOS options tab in the File → Open dialog, you will see that Auto distribute is set to Server Decompose.

It is probably easiest to describe the usage based on an example. So using the EnSight Gold format, lets run a simple model on two servers (computer1 and computer2). The files we will reference are:
cube.case (the EnSight Gold data file)
two_partitions.sos (the SOS casefile)
FORMAT type: master_server gold auto_distribute: on do_ghosts: on SERVERS number of servers: 2 #Server 1 #------------ machine id: computer1 executable: ensight_server data_path: /home/user/exodus casefile: cube.case #Server 2 #------------ machine id: computer1 executable: ensight_server data_path: /home/user/exodus casefile: cube.case
two_servers.res (the resource file, see Use Resource Management for more details)
#!CEIResourceFile 1.0 SOS: host: localhost SERVER: host: computer1 host: computer2
Make sure your cube.case data is available to the various machines on which you will run servers.
Create the two_partitions.sos sos casefile, or the two_servers.res resource file
Run EnSight like:
ensight -sosThen set the two_partitions.sos file in the File → Open dialog (format Case SOS). This enables you to load all parts, or select the ones to be loaded. Or use
ensight -sos two_partitions.soson the command line if you want to load all parts.-- or --
Open the cube.case file in the File → Open dialog (format Case), and place two_servers.res in the Set resource file field under the SOS options tab. This enables you to load all parts, or select the ones to be loaded. Or use
ensight -sos -res two_servers.reson the command line and set cube.case file in the File → Open dialog (format Case). Or useensight -sos -res two_servers.res cube.caseon the command line if you want to load all parts.There are several other variations that could be used, including the use of a manual connection with the SOS. They all have similar corresponding options.
This example deals with a EnSight Gold dataset that has been partitioned into 3 portions, each running on a different machine. The machines are named joe, sally, and bill. The data is not in the same location on all machines.
Note: The optional data_path line is used on two of the servers, but not the third.
FORMAT type: master_server gold SERVERS number of servers: 3 #Server 1 machine id: joe executable: ensight_server data_path: /usr/people/john/data casefile: portion_1.case #Server 2 is a Windows machine (notice .bat extension) machine id: sally executable: ensight_server.bat data_path: D:\john\data casefile: portion_2.case #Server 3 machine id: bill executable: ensight_server casefile: /scratch/temp/john/portion_3.case
If we name this example sos casefile - all.sos, and we run it on yet another machine - one named george, you would want the data distributed as follows:
On george: all.sos
On joe (in /usr/people/john/data): portion_1.case, and all files referenced by it.
On sally (in /scratch/sally/john/data): portion_2.case, and all files referenced by it.
On bill (in /scratch/temp/john): portion_3.case, and all file referenced by it.
By starting EnSight with the -sos command line option (which will
autoconnect using ensight.sos instead of
ensight_server), or by manually running
ensight.sos in place of ensight_server,
and providing all.sos as the casefile to read in the
Data Reader dialog - EnSight will actually start three
servers and compute the respective portions on them in parallel.
So, one could do the following (after preparing the all.sos file):
On george, run the client and the sos by invoking the
ensight script in a shell window (non-windows) or Command
Prompt window (windows), like:
george>> ensight
-sos
Or one could run the client on the myclient machine, telnet (or equivalent) into the george machine and run the sos there, by using the following commands:
|
If myclient is a non-windows machine: |
|
|
In a window on myclient: |
In a window that is telneted into the george machine: |
|
|
If george: is a non-windows machine: |
|
If george is a windows machine: |
|
If myclient is a windows machine: |
|
|
In a Command Prompt window on myclient: |
In a Command Prompt window that is telneted into the george machine: |
|
myclient>> ensight_client -cm |
If george: is a non-windows machine: |
|
If george is a windows machine: |
In either case, you would enter the all.sos command as the file to read in the Data Reader dialog once EnSight is up and connected. And the servers on joe, sally, and bill would be started and used automatically.
ENVIRONMENT Variables
The following Environment variables will directly affect the SOS performance, see Setup For Parallel Computation.
ENSIGHT10_MAX_THREADS
ENSIGHT10_MAX_SOSTHREADS
Additionally, rather than specifying whether unstructured ghost processing
and metric calculations will be done in an sos casefile, you can specify this via
command-line argument (-use_ghosts and
-use_metric), or via the following environment
variables. Remember that the ghost processing and metric calculation is defaulted
off.
UNSTRUCT_AUTODISTRIBUTE_USE GHOSTS 1 will set ghost processing on.
UNSTRUCT_AUTODISTRIBUTE_USE_METRIC 1 will set metric on.
The environment variable settings will take precedence over the command line arguments.
Optional NETWORK_INTERFACES Section Notes
If the machine named george had more than one network interface (say it had its main one named george, but also had one named george2), we could add the section shown below to our casefile example:
NETWORK_INTERFACES
number of network interfaces: 2
network interface: george
network interface: george2
This would cause machine joe to connect back to
george, machine sally to connect back to
george2, and machine bill to connect back to
george. This is because the sos will cycle through its
available network interfaces as it connects the servers. Remember that this is an
optional section, and most users will probably not use it. Also, the contents of
this section will be ignored if the -soshostname command
line option is used.
This example shows a plot3d dataset (post.x and post.q) that has not been partitioned, but is on an NFS mounted disk available to each server machine. EnSight will distribute the data to the 3 servers defined. IO will not necessarily be great since each server will be reading from the same file, but execution will be enhanced by the partitioning. We will use the same machines used in the previous example.
FORMAT type: master_server plot3d auto_distribute: on SERVERS number of servers: 3 #Server 1 machine id: joe executable: ensight_server data_path: /scratch/data casefile: post.x resfile: post.q #Server 2 machine id: sally executable: ensight_server data_path: /scratch/data casefile: post.x resfile: post.q #Server 3 machine id: bill executable: ensight_server data_path: /scratch/data casefile: post.x resfile: post.q
This example shows an EnSight Gold dataset (trial.case) that has not been partitioned, but is on an NFS mounted disk available to each server machine. EnSight will distribute the data to the 3 servers defined. IO will not necessarily be great since each server will be reading from the same file, but execution will be enhanced by the partitioning. We will use the same machines used in the previous examples.
FORMAT type: master_server gold auto_distribute: on do_ghosts: on buffer_size: 10000 want_metric: on SERVERS number of servers: 3 #Server 1 machine id: joe executable: ensight_server data_path: /scratch/data/gold casefile: trial.case #Server 2 machine id: sally executable: ensight_server data_path: /scratch/data/gold casefile: trial.case #Server 3 machine id: bill executable: ensight_server data_path: /scratch/data/gold casefile: trial.case
If using auto_distribute (and therefore each
server will be accessing the same data files), and the servers will all be run on
the same machine, then one can add the word repeat to the end
of the number of servers: num line and then only define one set
of Server info. For example:
FORMAT type: master_server gold auto_distribute: on SERVERS number of servers: 3 repeat #Server 1 machine id: joe executable: ensight_server data_path: /scratch/data/gold casefile: trial.case
If using structured auto_distribute, the default
decomposition scheme is to do so in the i, j, or k direction that has the largest
dimension. This may not always be the best direction for a given analysis.
Therefore, through the use of an environment variable, you can set the axis to use.
The chosen axis will be used unless the dimension in that direction will not allow
for all servers to contain data (namely, as long as the dimension in the chosen
direction is greater than the total number of servers used). To use the this option,
set the following to 0, 1, 2, or -1:
setenv SAD_DECOMPOSE_AXIS 0 (for the i axis) 1 (for the j axis) 2 (for the k axis) -1 (to use the default largest dimension scheme, same as not setting the variable)


