VM309
VM309
Torsional Buckling with Cruciform Section Beam
Test Case
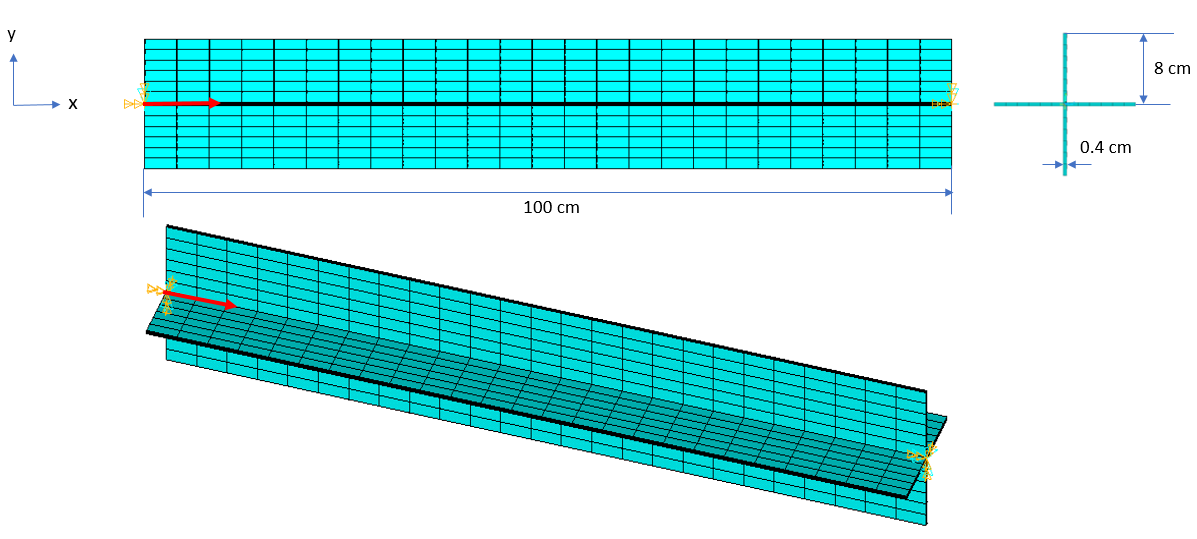
The beam is a cruciform section with four identical flanges of length 'l', width 'b' and thickness 't.' All the displacements and rotations at both ends of the beam are fixed, except for the x-displacement degrees of freedom where the axial force is applied. The warping degrees of freedom are activated but not constrained. Determine the critical buckling load for the first three modes.
| Material Properties | Geometric Properties | Loading |
|---|---|---|
|
E = 21000 kN/cm2 G = 8077 kN/cm2 |
Length, l = 100 cm Width, b = 8 cm Thickness, t = 0.4 cm Area = 12.64 cm2 Polar moment of Inertia = 273.24 cm4 Warping Constant = 3.6297 cm6 Torsional Constant = 0.69134 cm4 | F = 1 N at l = 0 |
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
The linear buckling analysis is solved using the PSTRES command. Doubly symmetric cross-section is used to demonstrate how an axial compressive load may cause purely torsional buckling.