RSM is able to integrate with established clusters and Cloud portals via configurations that you define directly in RSM. Information specified in an RSM configuration includes:
Details about the HPC resource to which jobs will be submitted, such as the domain name of a cluster submit host, or the URL of a Cloud portal
Client-to-HPC communication protocols
File transfer method (from client machine to HPC staging directory)
Queues to made available for simulation jobs
The RSM Configuration application provides a friendly, wizard-like interface that enables you to define RSM configurations quickly and easily. Defining a configuration involves a 3-part series of steps.
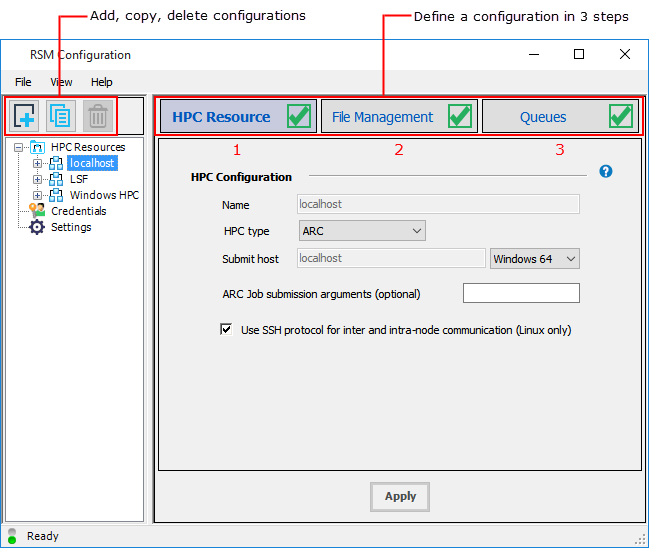
Initially, the list of HPC Resources will include a
localhost configuration, which is a basic, single-node Ansys
RSM Cluster (ARC) installed on the local machine. By default it has one RSM queue named
Local, which maps to an HPC queue named local.
This queue will run Ansys applications on the local machine.
Note: If you will be sharing your RSM configurations with other users, do not edit the existing
localhost configuration to create a new configuration. The
localhost configuration always refers to "the local machine", which
could be the cluster submit host or a user's local machine depending on where job submission is
being initiated.
If you want to run Ansys applications on machines other than the local machine, then you will need to create configurations for the HPC resources that you want to access (Ansys RSM Cluster, third-party cluster, Cloud portal).
The following topics provide a general overview of creating and managing RSM configurations:
For detailed information about setting up specific types of clusters, and creating RSM configurations for those cluster types, see Ansys RSM Cluster (ARC) Configuration and RSM Integration with a Cluster or Cloud Portal.


