Ansys Aqwa provides an engineering toolset for the investigation of the effects of wave, wind and current on floating and fixed offshore and marine structures, including: spars; floating production, storage, and offloading (FPSO) systems; semi-submersibles; tension leg platforms (TLPs); ships; renewable energy systems; and breakwater design.
Aqwa Hydrodynamic Diffraction provides an integrated environment for developing the primary hydrodynamic parameters required for undertaking complex motions and response analyses. Three-dimensional linear radiation and diffraction analysis may be undertaken with multiple bodies, taking full account of hydrodynamic interaction effects that occur between bodies. While primarily designed for floating structures, fixed bodies such as breakwaters or gravity-based structures may be included in the models. Computation of the second-order wave forces via the full quadratic transfer function matrices permits use over a wide range of water depths.
Aqwa Hydrodynamic Response provides dynamic analysis capabilities for undertaking global performance assessment of floating structures. A wide range of physical connections, such as mooring lines, fenders, and articulations, are provided to model the restraining conditions on the vessels. In addition, sea-keeping simulation may be undertaken with the inclusion of forward speed effects. Slow-drift effects and extreme-wave conditions may be investigated, and damage conditions, such as line breakage, may be included to study any transient effects that may occur.
Aqwa Hydrodynamic Diffraction and time domain Hydrodynamic Response calculations can also generate pressure and inertial loading for use in a structural analysis as part of the vessel hull design process. The results from a diffraction or time response analysis can be mapped onto an Ansys Mechanical finite element model for further structural assessment and detailed design. Since the mapping function automatically accounts for mesh differences between the hydrodynamic and finite element models, they do not have to be topologically identical.
- Important Information Regarding HTML-Based Results
If you use Internet Explorer or have this application installed on your machine, a conflict might occur with the HTML-based results in the Aqwa editor such as Hydrostatic, Frequency Domain Statistics, or Time Domain Statistics results. Examples of the errors are below:
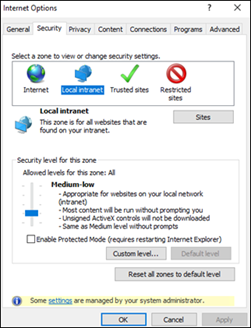
To resolve this issue, reconfigure the security levels to allow the Aqwa editor to evaluate the results by disabling Internet Explorer's enhanced security configuration, and enable ActiveX controls in the dialog box below: