Derived parameters are created using analytical expressions composed of input parameters, output parameters, or both input and output parameters. As the definition suggests, derived parameters are calculated from other parameters by using equations that you provide.
Some examples of derived parameters include:
Cost Function: Product of mass and cost per mass
Normalized Stress: Stress response divided by an applied stress
Average Value: Average of the first three frequencies
Mesh Sizing: Mesh parameter set as a function of a geometric parameter
Note: Derived parameters cannot reference other derived parameters.
Defining Derived Parameters
You can define derived parameters using various built-in arithmetic, trigonometric, and statistical functions. They are created in the analysis system and passed into DesignXplorer as output parameters.
To create a derived parameter:
Double-click the Parameter Set bar to open it.
Enter the expression in either of these locations:
Value field in the Outline pane
Expression field in the Properties pane (after selecting the parameter in the Outline pane)
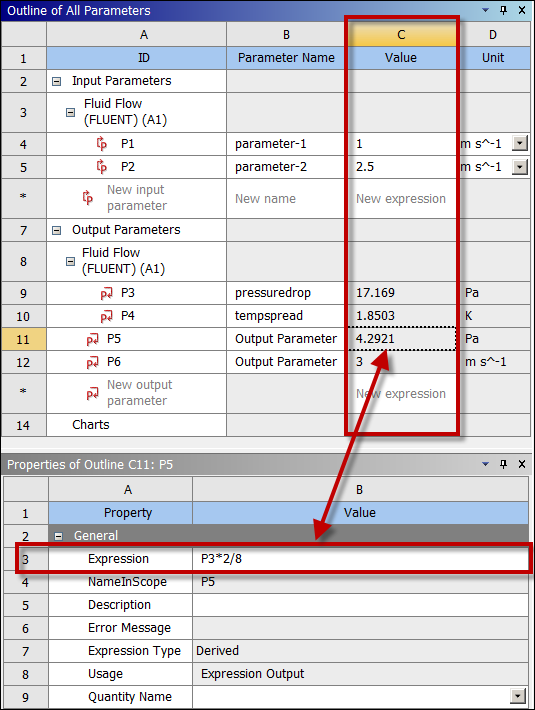
Note: You can add both derived parameters and constant values in the Outline pane. However, once derived parameters are added, they become read-only in the Outline pane. To edit them, you must use the Properties pane.


